ITF2 is a target of CXCR4 in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells and is associated with reduced survival in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer
- PMID: 20603605
- PMCID: PMC3040950
- DOI: 10.4161/cbt.10.6.12586
ITF2 is a target of CXCR4 in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells and is associated with reduced survival in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer
Abstract
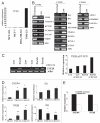
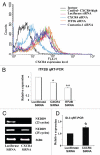
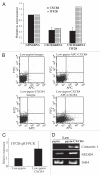
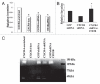
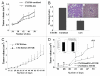
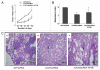
CXCR4, a chemokine receptor, plays an important role in breast cancer growth, invasion, and metastasis. The transcriptional targets of CXCR4 signaling are not known. Microarray analysis of CXCR4-enriched and CXCR4-low subpopulations of the MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell line, which has a constitutively active CXCR4 signaling network, revealed differential expression of ∼ 200 genes in the CXCR4-enriched subpopulation. ITF2, upregulated in CXCR4-enriched cells, was investigated further. Expression array datasets of primary breast tumors revealed higher ITF2 expression in estrogen receptor negative tumors, which correlated with reduced progression free and overall survival and suggested its relevance in breast cancer progression. CXCL12, a CXCR4 ligand, increased ITF2 expression in MDA-MB-231 cells. ITF2 is a basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor that controls the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and the function of the ID family (inhibitor-of-differentiation) of transcription factors, such as ID2. ID2 promotes differentiation of breast epithelial cells and its reduced expression in breast cancer is associated with an unfavorable prognosis. Both CXCR4 and ITF2 repressed ID2 expression. In xenograft studies, CXCR4-enriched cells formed large tumors and exhibited significantly elevated lung metastasis. Short interfering RNA against ITF2 reduced invasion of the CXCR4-enriched MDA-MB-231 subpopulation, whereas ITF2 overexpression restored the invasive capacity of MDA-MB-231 cells expressing CXCR4shRNA. Furthermore, overexpression of ITF2 in these cells enhanced tumor growth. We propose that ITF2 is one of the CXCR4 targets, which is involved in CXCR4-dependent tumor growth and invasion of breast cancer cells.
Figures


Comment in
-
CXCR4 signaling identifies a role for IFT2 in ER-negative breast cancers.Cancer Biol Ther. 2010 Sep 15;10(6):615-6. doi: 10.4161/cbt.10.6.12906. Epub 2010 Sep 7. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20686361 No abstract available.
References
-
- Steeg PS. Tumor metastasis: mechanistic insights and clinical challenges. Nat Med. 2006;12:895–904. - PubMed
-
- Balkwill F. Cancer and the chemokine network. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:540–550. - PubMed
-
- Orimo A, Gupta PB, Sgroi DC, Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Delaunay T, Naeem R, et al. Stromal fibroblasts present in invasive human breast carcinomas promote tumor growth and angiogenesis through elevated SDF-1/CXCL12 secretion. Cell. 2005;121:335–348. - PubMed
-
- Muller A, Homey B, Soto H, Ge N, Catron D, Buchanan ME, et al. Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis. Nature. 2001;410:50–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
