Cell adhesive behavior on thin polyelectrolyte multilayers: cells attempt to achieve homeostasis of its adhesion energy
- PMID: 20604583
- PMCID: PMC2918384
- DOI: 10.1021/la101689z
Cell adhesive behavior on thin polyelectrolyte multilayers: cells attempt to achieve homeostasis of its adhesion energy
Abstract
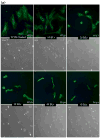
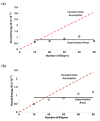
Linearly growing ultrathin polyelectrolyte multilayer (PEM) films of strong polyelectrolytes, poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) (PDAC), and sulfonated polystyrene, sodium salt (SPS) exhibit a gradual shift from cytophilic to cytophobic behavior, with increasing thickness for films of less than 100 nm. Previous explanations based on film hydration, swelling, and changes in the elastic modulus cannot account for the cytophobicity observed with these thin films as the number of bilayers increases. We implemented a finite element analysis to help elucidate the observed trends in cell spreading. The simulation results suggest that cells maintain a constant level of energy consumption (energy homeostasis) during active probing and thus respond to changes in the film stiffness as the film thickness increases by adjusting their morphology and the number of focal adhesions recruited and thereby their attachment to a substrate.
Figures






References
-
- Kidambi S, Lee I, Chan C. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 2004;126:16286–16287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

