A classification of diabetic foot infections using ICD-9-CM codes: application to a large computerized medical database
- PMID: 20604921
- PMCID: PMC2914721
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6963-10-192
A classification of diabetic foot infections using ICD-9-CM codes: application to a large computerized medical database
Abstract
Background: Diabetic foot infections are common, serious, and varied. Diagnostic and treatment strategies are correspondingly diverse. It is unclear how patients are managed in actual practice and how outcomes might be improved. Clarification will require study of large numbers of patients, such as are available in medical databases. We have developed and evaluated a system for identifying and classifying diabetic foot infections that can be used for this purpose.
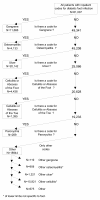
Methods: We used the (VA) Diabetes Epidemiology Cohorts (DEpiC) database to conduct a retrospective observational study of patients with diabetic foot infections. DEpiC contains computerized VA and Medicare patient-level data for patients with diabetes since 1998. We determined which ICD-9-CM codes served to identify patients with different types of diabetic foot infections and ranked them in declining order of severity: Gangrene, Osteomyelitis, Ulcer, Foot cellulitis/abscess, Toe cellulitis/abscess, Paronychia. We evaluated our classification by examining its relationship to patient characteristics, diagnostic procedures, treatments given, and medical outcomes.
Results: There were 61,007 patients with foot infections, of which 42,063 were classifiable into one of our predefined groups. The different types of infection were related to expected patient characteristics, diagnostic procedures, treatments, and outcomes. Our severity ranking showed a monotonic relationship to hospital length of stay, amputation rate, transition to long-term care, and mortality.
Conclusions: We have developed a classification system for patients with diabetic foot infections that is expressly designed for use with large, computerized, ICD-9-CM coded administrative medical databases. It provides a framework that can be used to conduct observational studies of large numbers of patients in order to examine treatment variation and patient outcomes, including the effect of new management strategies, implementation of practice guidelines, and quality improvement initiatives.
Figures
References
-
- International Classification of Diseases tR, Clinical Modification. Medicode. 5 1996.
-
- Prompers L, Huijberts M, Apelqvist J, Jude E, Piaggesi A, Bakker K, Edmonds M, Holstein P, Jirkovska A, Mauricio D. High prevalence of ischaemia, infection and serious comorbidity in patients with diabetic foot disease in Europe. Baseline results from the Eurodiale study. Diabetologia. 2007;50(1):18–25. doi: 10.1007/s00125-006-0491-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Newman LG, Waller J, Palestro CJ, Schwartz M, Klein MJ, Hermann G, Harrington E, Harrington M, Roman SH, Stagnaro-Green A. Unsuspected osteomyelitis in diabetic foot ulcers. Diagnosis and monitoring by leukocyte scanning with indium in 111 oxyquinoline. Jama. 1991;266(9):1246–1251. doi: 10.1001/jama.266.9.1246. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical