Transcriptional regulation of renal cytoprotective genes by Nrf2 and its potential use as a therapeutic target to mitigate cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity
- PMID: 20605904
- PMCID: PMC2957774
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.110.170084
Transcriptional regulation of renal cytoprotective genes by Nrf2 and its potential use as a therapeutic target to mitigate cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity
Abstract
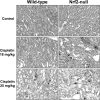
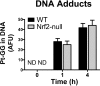
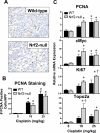
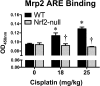
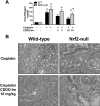
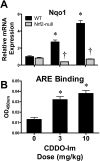
The use of the chemotherapeutic drug cisplatin is limited in part by nephrotoxicity. Cisplatin causes renal DNA adducts and oxidative stress in rodents. The transcription factor Nrf2 (nuclear factor E2-related factor 2) induces expression of cytoprotective genes, including Nqo1 (NADPH:quinone oxidoreductase 1), Ho-1 (heme oxygenase-1), and Gclc (glutamate cysteine ligase catalytic subunit), in response to electrophilic and oxidative stress. In the present study, plasma and kidneys from wild-type and Nrf2-null mice were collected after receiving cisplatin for evaluation of renal injury, inflammation, mRNA, and protein expression. Compared with wild types, more extensive nephrotoxicity was observed in Nrf2-null mice after cisplatin treatment. Kidneys from Nrf2-null mice treated with cisplatin had more neutrophil infiltration accompanied by increased p65 nuclear factor κB binding and elevated inflammatory mediator mRNA levels. Cisplatin increased renal mRNA and protein expression of cytoprotective genes (Nqo1, Ho-1, Gclc) and transporters Mrp2 and Mrp4 in wild-type but not in Nrf2-null mice. Lastly, the Nrf2 activator, CDDO-Im [2-cyano-3,12-dioxooleana-1,9-dien-28-oic imidazolide], increased Nrf2 signaling in kidneys from wild-type mice and protected them from cisplatin toxicity. Collectively, these data indicate that the absence of Nrf2 exacerbates cisplatin renal damage and that pharmacological activation of Nrf2 may represent a novel therapy to prevent kidney injury. Coordinated regulation of detoxification enzymes and drug transporters and suppression of inflammation by Nrf2 during cisplatin nephrotoxicity are probable defense mechanisms to eliminate toxic mediators and promote proximal tubule recovery.
Figures






References
-
- Aleksunes LM, Manautou JE. (2007) Emerging role of Nrf2 in protecting against hepatic and gastrointestinal disease. Toxicol Pathol 35:459–473 - PubMed
-
- Boesch-Saadatmandi C, Wagner AE, Graeser AC, Hundhausen C, Wolffram S, Rimbach G. (2009) Ochratoxin A impairs Nrf2-dependent gene expression in porcine kidney tubulus cells. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl) 93:547–554 - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Shaikh ZA. (2009) Activation of Nrf2 by cadmium and its role in protection against cadmium-induced apoptosis in rat kidney cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 241:81–89 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RR021940/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES009716/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 ES007079/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- ES013714/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- K99 ES018885/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK081461/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES009649/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR021940/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK081461/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- ES007079/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- ES009649/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- DK080774/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES013714/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DK080774/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- ES009716/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DK080774/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

