International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXV. Nomenclature, classification, and pharmacology of G protein-coupled melatonin receptors
- PMID: 20605968
- PMCID: PMC2964901
- DOI: 10.1124/pr.110.002832
International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXV. Nomenclature, classification, and pharmacology of G protein-coupled melatonin receptors
Abstract
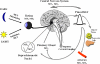
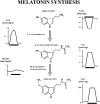
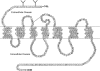
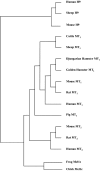
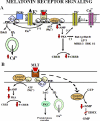
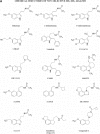
The hormone melatonin (5-methoxy-N-acetyltryptamine) is synthesized primarily in the pineal gland and retina, and in several peripheral tissues and organs. In the circulation, the concentration of melatonin follows a circadian rhythm, with high levels at night providing timing cues to target tissues endowed with melatonin receptors. Melatonin receptors receive and translate melatonin's message to influence daily and seasonal rhythms of physiology and behavior. The melatonin message is translated through activation of two G protein-coupled receptors, MT(1) and MT(2), that are potential therapeutic targets in disorders ranging from insomnia and circadian sleep disorders to depression, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer. This review summarizes the steps taken since melatonin's discovery by Aaron Lerner in 1958 to functionally characterize, clone, and localize receptors in mammalian tissues. The pharmacological and molecular properties of the receptors are described as well as current efforts to discover and develop ligands for treatment of a number of illnesses, including sleep disorders, depression, and cancer.
Figures



References
-
- Al-Ghoul WM, Herman MD, Dubocovich ML. (1998) Melatonin receptor subtype expression in human cerebellum. Neuroreport 9:4063–4068 - PubMed
-
- Alonso-Vale MI, Andreotti S, Peres SB, Anhê GF, das Neves Borges-Silva C, Neto JC, Lima FB. (2005) Melatonin enhances leptin expression by rat adipocytes in the presence of insulin. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 288:E805–E812 - PubMed
-
- Arendt J. (2000) Melatonin, circadian rhythms, and sleep. N Engl J Med 343:1114–1116 - PubMed
-
- Arendt J, Skene DJ. (2005) Melatonin as a chronobiotic. Sleep Med Rev 9:25–39 - PubMed
-
- Arnis S, Fahmy K, Hofmann KP, Sakmar TP. (1994) A conserved carboxylic acid group mediates light-dependent proton uptake and signaling by rhodopsin. J Biol Chem 269:23879–23881 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

