Interleukin 6 mediates myocardial fibrosis, concentric hypertrophy, and diastolic dysfunction in rats
- PMID: 20606113
- PMCID: PMC2921860
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.148635
Interleukin 6 mediates myocardial fibrosis, concentric hypertrophy, and diastolic dysfunction in rats
Abstract
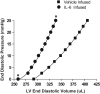
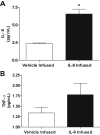
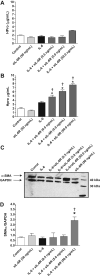
Although there is a correlation between hypertension and levels of interleukin (IL) 6, the exact role this cytokine plays in myocardial remodeling is unknown. This is complicated by the variable tissue and circulating levels of IL-6 reported in numerous experimental models of hypertension. Accordingly, we explored the hypothesis that elevated levels of IL-6 mediate adverse myocardial remodeling. To this end, adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were infused with IL-6 (2.5 microg . kg(-1) . h(-1), IP) for 7 days via osmotic minipump and compared with vehicle-infused, aged-matched controls. Left ventricular function was evaluated using a blood-perfused isolated heart preparation. Myocardial interstitial collagen volume fraction and isolated cardiomyocyte size were also assessed. Isolated adult cardiac fibroblast experiments were performed to determine the importance of the soluble IL-6 receptor in mediating cardiac fibrosis. IL-6 infusions in vivo resulted in concentric left ventricular hypertrophy, increased ventricular stiffness, a marked increase in collagen volume fraction (6.2% versus 1.7%; P<0.001), and proportional increases in cardiomyocyte width and length, all independent of blood pressure. The soluble IL-6 receptor in combination with IL-6 was found to be essential to producing increased collagen concentration by isolated cardiac fibroblasts and also played a role in mediating a phenotypic conversion to myofibroblasts. These novel observations demonstrate that IL-6 induces a myocardial phenotype almost identical to that of the hypertensive heart, identifying IL-6 as potentially important in this remodeling process.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
The soluble interleukin 6 receptor takes its place in the pantheon of interleukin 6 signaling proteins: phenoconversion of cardiac fibroblasts to myofibroblasts.Hypertension. 2010 Aug;56(2):193-5. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.154609. Epub 2010 Jul 6. Hypertension. 2010. PMID: 20606105 No abstract available.
References
-
- Levick SP, McLarty JL, Murray DB, Freeman RM, Carver WE, Brower GL. Cardiac mast cells mediate left ventricular fibrosis in the hypertensive rat heart. Hypertension. 2009;53:1041–1047. - PubMed
-
- Hinglais N, Huedes D, Nicoletti A, Manset C, Laurent M, Bariety J, Michel JB. Colocalization of myocardial fibrosis and inflammatory cells in rats. Lab Invest. 1994;70:286–294. - PubMed
-
- Tomita H, Egashira K, Kubo-Inoue M, Usui M, Koyanagi M, Shimokawa H, Takeya M, Yoshimura T, Takeshita A. Inhibition of NO synthesis induces inflammatory changes and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression in rat hearts and vessels. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 1998;18:1456–1464. - PubMed
-
- Koyanagi M, Egashira K, Kitamoto S, Ni W, Shimokawa H, Takeya M, Yoshimura T, Takeshita A. Role of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in cardiovascular remodeling induced by chronic blockade of nitric oxide synthesis. Circulation. 2000;102:2243–2248. - PubMed
-
- Kagitani S, Ueno H, Hirade S, Takahashi T, Takata M, Inoue H. Tranilast attenuates myocardial fibrosis in association with suppression of monocyte/macrophage infiltration in DOCA/salt hypertensive rats. J Hypertens. 2004;22:1007–1015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

