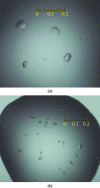
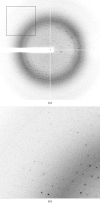
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of human endonuclease 1 (APE1) in complex with an oligonucleotide containing a 5,6-dihydrouracil (DHU) or an alpha-anomeric 2'-deoxyadenosine (alphadA) modified base
- PMID: 20606276
- PMCID: PMC2898464
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309110017021
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of human endonuclease 1 (APE1) in complex with an oligonucleotide containing a 5,6-dihydrouracil (DHU) or an alpha-anomeric 2'-deoxyadenosine (alphadA) modified base
Abstract
The multifunctional human apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) endonuclease 1 (APE1) is a key enzyme involved in both the base-excision repair (BER) and nucleotide-incision repair (NIR) pathways. In the NIR pathway, APE1 incises DNA 5' to a number of oxidatively damaged bases. APE1 was crystallized in the presence of a 15-mer DNA containing an oxidatively damaged base in a single central 5,6-dihydrouracil (DHU).T or alpha-anomeric 2'-deoxyadenosine (alphadA).T base pair. Diffraction data sets were collected to 2.2 and 2.7 A resolution from DNA-DHU-APE1 and DNA-alphadA-APE1 crystals, respectively. The crystals were isomorphous and contained one enzyme molecule in the asymmetric unit. Molecular replacement was performed and the initial electron-density maps revealed that in both complexes APE1 had crystallized with a degradation DNA product reduced to a 6-mer, suggesting that NIR and exonuclease reactions occurred prior to crystallization.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A kinetic mechanism of repair of DNA containing α-anomeric deoxyadenosine by human apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1.Mol Biosyst. 2016 Oct 18;12(11):3435-3446. doi: 10.1039/c6mb00511j. Mol Biosyst. 2016. PMID: 27722620
-
Structural comparison of AP endonucleases from the exonuclease III family reveals new amino acid residues in human AP endonuclease 1 that are involved in incision of damaged DNA.Biochimie. 2016 Sep-Oct;128-129:20-33. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2016.06.011. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Biochimie. 2016. PMID: 27343627
-
The major Arabidopsis thaliana apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease, ARP is involved in the plant nucleotide incision repair pathway.DNA Repair (Amst). 2016 Dec;48:30-42. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2016.10.009. Epub 2016 Oct 29. DNA Repair (Amst). 2016. PMID: 27836324
-
Inhibitors of nuclease and redox activity of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1/redox effector factor 1 (APE1/Ref-1).Bioorg Med Chem. 2017 May 1;25(9):2531-2544. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2017.01.028. Epub 2017 Jan 21. Bioorg Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28161249 Review.
-
Functions of the major abasic endonuclease (APE1) in cell viability and genotoxin resistance.Mutagenesis. 2020 Feb 13;35(1):27-38. doi: 10.1093/mutage/gez046. Mutagenesis. 2020. PMID: 31816044 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Insight into mechanisms of 3'-5' exonuclease activity and removal of bulky 8,5'-cyclopurine adducts by apurinic/apyrimidinic endonucleases.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Aug 13;110(33):E3071-80. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1305281110. Epub 2013 Jul 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23898172 Free PMC article.
-
α-D-2'-Deoxyadenosine, an irradiation product of canonical DNA and a component of anomeric nucleic acids: crystal structure, packing and Hirshfeld surface analysis.Acta Crystallogr C Struct Chem. 2024 Feb 1;80(Pt 2):21-29. doi: 10.1107/S2053229624000457. Epub 2024 Jan 22. Acta Crystallogr C Struct Chem. 2024. PMID: 38252461 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beernink, P. T., Segelke, B. W., Hadi, M. Z., Erzberger, J. P., Wilson, D. M. III & Rupp, B. (2001). J. Mol. Biol.307, 1023–1034. - PubMed
-
- Cadet, J., Douki, T., Gasparutto, D. & Ravanat, J. L. (2003). Mutat. Res.531, 5–23. - PubMed
-
- Chou, K.-M. & Cheng, Y.-C. (2002). Nature (London), 415, 655–659. - PubMed
-
- Collaborative Computational Project, Number 4 (1994). Acta Cryst. D50, 760–763. - PubMed
-
- Daviet, S., Couve-Privat, S., Gros, L., Shinozuka, K., Ide, H., Saparbaev, M. & Ishchenko, A. A. (2007). DNA Repair, 6, 8–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous