A phase I study of aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase gene therapy for Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 20606642
- PMCID: PMC2956925
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2010.135
A phase I study of aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase gene therapy for Parkinson's disease
Abstract
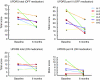
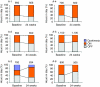
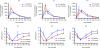
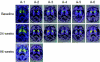
Gene transfer of dopamine-synthesizing enzymes into the striatal neurons has led to behavioral recovery in animal models of Parkinson's disease (PD). We evaluated the safety, tolerability, and potential efficacy of adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector-mediated gene delivery of aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) into the putamen of PD patients. Six PD patients were evaluated at baseline and at 6 months, using multiple measures, including the Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS), motor state diaries, and positron emission tomography (PET) with 6-[(18)F]fluoro-L-m-tyrosine (FMT), a tracer for AADC. The short-duration response to levodopa was measured in three patients. The procedure was well tolerated. Six months after surgery, motor functions in the OFF-medication state improved an average of 46% based on the UPDRS scores, without apparent changes in the short-duration response to levodopa. PET revealed a 56% increase in FMT activity, which persisted up to 96 weeks. Our findings provide class IV evidence regarding the safety and efficacy of AADC gene therapy and warrant further evaluation in a randomized, controlled, phase 2 setting.
Figures
References
-
- Fahn S. The history of dopamine and levodopa in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2008;23 Suppl 3:S497–S508. - PubMed
-
- Nagatsu T., and, Sawada M. Biochemistry of postmortem brains in Parkinson's disease: historical overview and future prospects. J Neural Transm Suppl. 2007. pp. 113–120. - PubMed
-
- Bankiewicz KS, Eberling JL, Kohutnicka M, Jagust W, Pivirotto P, Bringas J, et al. Convection-enhanced delivery of AAV vector in parkinsonian monkeys; in vivo detection of gene expression and restoration of dopaminergic function using pro-drug approach. Exp Neurol. 2000;164:2–14. - PubMed
-
- Bankiewicz KS, Forsayeth J, Eberling JL, Sanchez-Pernaute R, Pivirotto P, Bringas J, et al. Long-term clinical improvement in MPTP-lesioned primates after gene therapy with AAV-hAADC. Mol Ther. 2006;14:564–570. - PubMed
-
- Muramatsu S, Fujimoto K, Ikeguchi K, Shizuma N, Kawasaki K, Ono F, et al. Behavioral recovery in a primate model of Parkinson's disease by triple transduction of striatal cells with adeno-associated viral vectors expressing dopamine-synthesizing enzymes. Hum Gene Ther. 2002;13:345–354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

