Protective effects of Allium sativum against defects of hypercholesterolemia on pregnant rats and their offspring
- PMID: 20607041
- PMCID: PMC2894650
Protective effects of Allium sativum against defects of hypercholesterolemia on pregnant rats and their offspring
Abstract
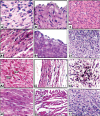
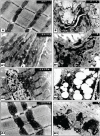
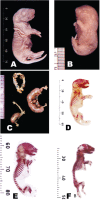
Sixty fertile female and male albino rats of Wistar strain (I male/ 3 females) were used in the present study. The females were divided into four groups of ten rats each. Group 1 received water and standard feeds for thirty-four days. Group 2 was fed with a cholesterol-containing diet (1%) for two weeks prior to onset of gestation and maintained administration till parturition, produce atherosclerosis (34 days). Group 3 received intragastric administration of 100mg homogenate of garlic (Allium sativum)/kg body weight for three weeks prior to onset of gestation as well as throughout the gestation period. Group 4 intragastrically administered garlic for one week of group B and maintained with combined garlic-treatment for the mentioned period. At parturition, the pregnant were sacrificed and serum total cholesterol (TCL), triglycerides (TG), HDL, LDL and creatine kinase activity (CK) were determined. The total numbers of offspring were recorded and examined morphological for congenital abnormalities. Biopsies of heart and dorsal aorta of both pregnant and their offspring (1 day-age) were processed for investigation at light and transmission electron microscopy. The skeleton of the newborn of different experimental groups were stained with alizarin red s and mor-phometric assessment of mandibular and appendicular bone length. The study revealed that the myocardium of atherosclerotic mother exhibited leuhkocytic inflammatory cell infiltration associated with necrosis, eosinophilia of myocardiai fibers, and edema of blood vessels. Ultrastructural studies revealed swelling of mitochondria, disruption of cristae in the myocardiai muscle fibers. The dorsal aorta possessed accumulation of extra-cellular lipid in intima lining of endothelium. The collagenous fibrils in the tunica adventitia became fragile and loosely separated from each other. Numerous foamy lipid loaden cells were detected within the tunica intima causing deterioration of the elastic fibers, resulting in fibrinoid necrosis. Oral supplementation with Allium sativum (100 mg/ kg) ameliorated these effects in myocardium muscle of mothers and offspring; however the dorsal aorta of mothers showed partial amelioration. Hypercholesterolemic mothers exhibited marked alterations in serum TCL, TG, LDL and CK activity. Supplementation with Allium sativum ameliorated the drastic biochemical alterations. Concerning pregnancy, hypercholesterolemia increased the incidence of abortion and abnormalities of the newborn including decreased body weight, reduced ossification of axial (mandible) and appendicular bones. All these effects were markedly ameliorated by supplementation with Allium sativum. The author finally concluded that hypercholesterolemia exhibits pathological alterations of myocardiai muscles reducing its optimal capacity for pumping blood to different body organs along with atherosclerosis of dorsal aorta which intern affect the progress of gestation and development of both morphological and skeletal abnormalities. Allium sativum-supplementation leads to amelioration of both mother and their offspring investigated parameters as a result of its antioxidant activity.
Keywords: Allium sativum; Hypercholersterolemia; cardiovascular; offspring; pregnant rats.
Figures
References
-
- Goldstein JL, Hobbs HH, Brown MS. Familial Hypercholesterolemia. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D, editors. The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease. 8th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2001. pp. 2863–2913.
-
- Vattikuti R, Towler DA. osteogenic regulation of vascular calcification: an early perspective. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2004;286(5):E686–96. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz CJ, Valente AJ, Sprague EA, Kelley JL, Nerem RM. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: an overview. Clin Cardiol. 1991;14(1):1–16. - PubMed
-
- Blania G, Spangenberg B. Formation of allicin from dried garlic (Allium sativum): a simple HPTLC ethod for simultaneous determination of allicin and ajoene in dried garlic and garlic preparations. Planta Med. 1991;57(4):371–375. - PubMed
-
- Newall CA, Anderson LA, Phillipson JD. ix. London: Pharmaceutical Press; 1996. Herbal medicines: a guide for health-care professionals; p. 296.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
