Effects of blood glutamate scavenging on cortical evoked potentials
- PMID: 20607387
- PMCID: PMC11498888
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-010-9542-8
Effects of blood glutamate scavenging on cortical evoked potentials
Abstract
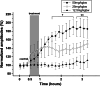
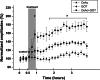
It is well known that traumatic or ischemic brain injury is followed by acute excitotoxicity caused by the presence of abnormally high glutamate (Glu) in brain fluids. It has recently been demonstrated that excess Glu can be eliminated from brain into blood following the intravenous administration of oxaloacetate (OxAc), which, by scavenging blood Glu, induces an enhanced and neuroprotective brain-to-blood Glu efflux. In this study, we subjected rats to intravenous OxAc administration (i.v., 12.5, 25, and 50 mg/kg, respectively), and studied its effects on somatosensory evoked cortical potentials (EPs). Against our expectation, the amplitudes of EPs did not decrease but increased in a dose- and time-dependent manner after OxAc administration. Similar effects were observed when blood Glu scavenging was enhanced by combining OxAc (12.5 mg/kgbw) with recombinant glutamate-oxaloacetate transaminase (GOT, 0.14 nmol/100 g rat). On the basis of these results, we suggest that the changes of amplitudes of the EPs involve not only a glutamatergic but also the weakening of a GABAergic component. We cannot rule out the possibility that OxAc penetrates into the brain and improves mitochondrial functions.
Figures
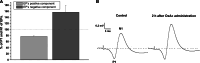
Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective effect of oxaloacetate in a focal brain ischemic model in the rat.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2015 Jan;35(1):17-22. doi: 10.1007/s10571-014-0064-7. Epub 2014 May 8. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 24807461 Free PMC article.
-
Oxaloacetate decreases the infarct size and attenuates the reduction in evoked responses after photothrombotic focal ischemia in the rat cortex.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2009 Sep;29(6-7):827-35. doi: 10.1007/s10571-009-9364-8. Epub 2009 Mar 4. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2009. PMID: 19259807 Free PMC article.
-
Brain neuroprotection by scavenging blood glutamate.Exp Neurol. 2007 Jan;203(1):213-20. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2006.08.021. Epub 2006 Oct 2. Exp Neurol. 2007. PMID: 17014847
-
Extracorporeal methods of blood glutamate scavenging: a novel therapeutic modality.Expert Rev Neurother. 2015 May;15(5):501-508. doi: 10.1586/14737175.2015.1032259. Epub 2015 Apr 12. Expert Rev Neurother. 2015. PMID: 25865745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain to blood glutamate scavenging as a novel therapeutic modality: a review.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2014 Aug;121(8):971-9. doi: 10.1007/s00702-014-1181-7. Epub 2014 Mar 13. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2014. PMID: 24623040 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The potential role of kynurenines in Alzheimer's disease: pathomechanism and therapeutic possibilities by influencing the glutamate receptors.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2014 Aug;121(8):881-9. doi: 10.1007/s00702-013-1135-5. Epub 2013 Dec 18. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2014. PMID: 24346138 Review.
-
Neuroprotective effect of oxaloacetate in a focal brain ischemic model in the rat.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2015 Jan;35(1):17-22. doi: 10.1007/s10571-014-0064-7. Epub 2014 May 8. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 24807461 Free PMC article.
-
Amelioration of ischemic brain damage by peritoneal dialysis.J Clin Invest. 2013 Oct;123(10):4359-63. doi: 10.1172/JCI67284. Epub 2013 Sep 3. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 23999426 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamate as a neurotransmitter in the healthy brain.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2014 Aug;121(8):799-817. doi: 10.1007/s00702-014-1180-8. Epub 2014 Mar 1. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2014. PMID: 24578174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood Glutamate Reducing Effect of Hemofiltration in Critically Ill Patients.Neurotox Res. 2018 Feb;33(2):300-308. doi: 10.1007/s12640-017-9791-0. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Neurotox Res. 2018. PMID: 28836163 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Belan PV, Kostyuk PG (2002) Glutamate-receptor-induced modulation of GABAergic synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. Pflugers Arch 444:26–37 - PubMed
-
- Castillo J, Davalos A, Naveiro J, Noya M (1996) Neuroexcitatory amino acids and their relation to infarct size and neurological deficit in ischemic stroke. Stroke 27:1060–1065 - PubMed
-
- Danbolt NC (2001) Glutamate uptake. Prog Neurobiol 65:1–105 - PubMed
-
- Engelman HS, MacDermott AB (2004) Presynaptic ionotropic receptors and control of transmitter release. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:135–145 - PubMed
-
- Farazifard R, Wu SH (2010) Metabotropic glutamate receptors modulate glutamatergic and GABAergic synaptic transmission in the central nucleus of the inferior colliculus. Brain Res 1325:28–40 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

