Emergence of chemical biology approaches to the RNAi/miRNA pathway
- PMID: 20609408
- PMCID: PMC2901241
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.05.014
Emergence of chemical biology approaches to the RNAi/miRNA pathway
Abstract
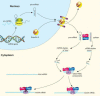
RNA interference (RNAi) is a well-conserved mechanism that uses small noncoding RNAs to silence gene expression posttranscriptionally. Gene regulation by RNAi is now recognized as one of the major regulatory pathways in eukaryotic cells. Although the main components of the RNAi/miRNA pathway have been identified, the molecular mechanisms regulating the activity of the RNAi/miRNA pathway have only begun to emerge within the last couple of years. Recently, high-throughput reporter assays to monitor the activity of the RNAi/miRNA pathway have been developed and used for proof-of-concept pilot screens. Both inhibitors and activators of the RNAi/miRNA pathway have been found. Although still in its infancy, a chemical biology approach using high-throughput chemical screens should open up a new avenue for dissecting the RNAi/miRNA pathway, as well as developing novel RNAi- or miRNA-based therapeutic interventions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Probing the microRNA pathway with small molecules.Bioorg Med Chem. 2013 Oct 15;21(20):6119-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2013.05.030. Epub 2013 May 25. Bioorg Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23791866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A small molecule enhances RNA interference and promotes microRNA processing.Nat Biotechnol. 2008 Aug;26(8):933-40. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1481. Epub 2008 Jul 20. Nat Biotechnol. 2008. PMID: 18641635 Free PMC article.
-
Small molecule modifiers of the microRNA and RNA interference pathway.AAPS J. 2010 Mar;12(1):51-60. doi: 10.1208/s12248-009-9159-3. Epub 2009 Nov 25. AAPS J. 2010. PMID: 19937410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bottlenecks caused by software gaps in miRNA and RNAi research.Pharm Res. 2012 Jul;29(7):1717-21. doi: 10.1007/s11095-012-0712-x. Epub 2012 Feb 24. Pharm Res. 2012. PMID: 22362409
-
Approaches to the modulation of miRNA maturation.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1095:27-58. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-703-7_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24166301 Review.
Cited by
-
Dicer functions in aquatic species.J Amino Acids. 2011;2011:782187. doi: 10.4061/2011/782187. Epub 2011 Jun 9. J Amino Acids. 2011. PMID: 22312469 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosing and Treating Nervous System Disorders by Targeting Novel Classes of Non-coding RNAs.Int Drug Discov. 2011 Jun-Jul;6(3):30-36. Int Drug Discov. 2011. PMID: 26659096 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Emerging roles of non-coding RNAs in brain evolution, development, plasticity and disease.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012 Jul 20;13(8):528-41. doi: 10.1038/nrn3234. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22814587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Simulation Studies of 3,3'-Diindolylmethane as a Potent MicroRNA-21 Antagonist.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2017 Oct-Dec;9(4):259-265. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.JPBS_266_16. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2017. PMID: 29456377 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic mechanisms governing the process of neurodegeneration.Mol Aspects Med. 2013 Jul-Aug;34(4):875-82. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2012.06.011. Epub 2012 Jul 7. Mol Aspects Med. 2013. PMID: 22782013 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

