Lipid-induced insulin resistance: unravelling the mechanism
- PMID: 20609972
- PMCID: PMC2995547
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60408-4
Lipid-induced insulin resistance: unravelling the mechanism
Abstract
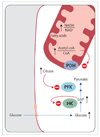
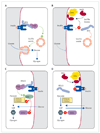
Insulin resistance has long been associated with obesity. More than 40 years ago, Randle and colleagues postulated that lipids impaired insulin-stimulated glucose use by muscles through inhibition of glycolysis at key points. However, work over the past two decades has shown that lipid-induced insulin resistance in skeletal muscle stems from defects in insulin-stimulated glucose transport activity. The steatotic liver is also resistant to insulin in terms of inhibition of hepatic glucose production and stimulation of glycogen synthesis. In muscle and liver, the intracellular accumulation of lipids-namely, diacylglycerol-triggers activation of novel protein kinases C with subsequent impairments in insulin signalling. This unifying hypothesis accounts for the mechanism of insulin resistance in obesity, type 2 diabetes, lipodystrophy, and ageing; and the insulin-sensitising effects of thiazolidinediones.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Prentice AM, Hennig BJ, Fulford AJ. Evolutionary origins of the obesity epidemic: natural selection of thrifty genes or genetic drift following predation release? Int J Obes (Lond) 2008;32:1607–1610. - PubMed
-
- Harris JL, Pomeranz JL, Lobstein T, Brownell KD. A crisis in the marketplace: how food marketing contributes to childhood obesity and what can be done. Annu Rev Public Health. 2009;30:211–225. - PubMed
-
- Diet, nutrition and the prevention of chronic diseases. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 2003;916:1–149. - PubMed
-
- Mendez MA, Monteiro CA, Popkin BM. Overweight exceeds underweight among women in most developing countries. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005;81:714–721. - PubMed
-
- Sherry B, Mei Z, Scanlon KS, Mokdad AH, Grummer-Strawn LM. Trends in state-specific prevalence of overweight and underweight in 2- through 4-year-old children from low-income families from 1989 through 2000. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2004;158:1116–1124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 RR024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK-59635/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG023686/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- P01 DK-068229/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK068229/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK040936/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023686/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK045735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG-23686,/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK-45735,/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 RR017404/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK049230/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK-49230,/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK-40936/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 RR17404/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR-024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059635/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

