Identification of novel mutations responsible for resistance to MK-2048, a second-generation HIV-1 integrase inhibitor
- PMID: 20610719
- PMCID: PMC2937597
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01164-10
Identification of novel mutations responsible for resistance to MK-2048, a second-generation HIV-1 integrase inhibitor
Abstract
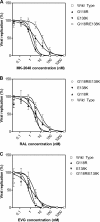
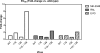
MK-2048 represents a prototype second-generation integrase strand transfer inhibitor (INSTI) developed with the goal of retaining activity against viruses containing mutations associated with resistance to first-generation INSTIs, raltegravir (RAL) and elvitegravir (EVG). Here, we report the identification of mutations (G118R and E138K) which confer resistance to MK-2048 and not to RAL or EVG. These mutations were selected in vitro and confirmed by site-specific mutagenesis. G118R, which appeared first in cell culture, conferred low levels of resistance to MK-2048. G118R also reduced viral replication capacity to approximately 1% that of the isogenic wild-type (wt) virus. The subsequent selection of E138K partially restored replication capacity to approximately 13% of wt levels and increased resistance to MK-2048 to approximately 8-fold. Viruses containing G118R and E138K remained largely susceptible to both RAL and EVG, suggesting a unique interaction between this second-generation INSTI and the enzyme may be defined by these residues as a potential basis for the increased intrinsic affinity and longer "off" rate of MK-2048. In silico structural analysis suggests that the introduction of a positively charged arginine at position 118, near the catalytic amino acid 116, might decrease Mg(2+) binding, compromising enzyme function and thus leading to the significant reduction in both integration and viral replication capacity observed with these mutations.
Figures


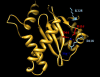

References
-
- Chen, X., M. Tsiang, F. Yu, M. Hung, G. S. Jones, A. Zeynalzadegan, X. Qi, H. Jin, C. U. Kim, S. Swaminathan, and J. M. Chen. 2008. Modeling, analysis, and validation of a novel HIV integrase structure provide insights into the binding modes of potent integrase inhibitors. J. Mol. Biol. 380:504-519. - PubMed
-
- DeLano, W. L. 2002. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System.
-
- Delelis, O., I. Malet, L. Na, L. Tchertanov, V. Calvez, A.-G. Marcelin, F. Subra, E. Deprez, and J.-F. Mouscadet. 2009. The G140S mutation in HIV integrases from raltegravir-resistant patients rescues catalytic defect due to the resistance Q148H mutation. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:1193-1201. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

