Early progenitor cell marker expression distinguishes type II from type I focal cortical dysplasias
- PMID: 20613634
- PMCID: PMC3474261
- DOI: 10.1097/NEN.0b013e3181eac1f5
Early progenitor cell marker expression distinguishes type II from type I focal cortical dysplasias
Abstract
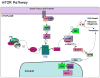
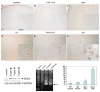
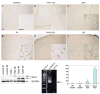
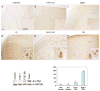
Type I and type II focal cortical dysplasias (FCDs) exhibit distinct histopathologic features that suggest different pathogenic mechanisms. Type I FCDs are characterized by mild laminar disorganization and hypertrophic neurons, whereas type II FCDs exhibit dramatic laminar disorganization and cytomegalic cells (balloon cells). Both FCD types are associated with intractable epilepsy; therefore, identifying cellular or molecular differences between these lesion types that explains the histologic differences could provide new diagnostic and therapeutic insights. Type II FCDs express nestin, a neuroglial progenitor protein that is modulated in vitro by the stem cell proteins c-Myc, sex-determining region Y-box 2 (SOX2), and Octamer-4 (Oct-4) after activation of mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1). Because mTORC1 activation has been demonstrated in type II FCDs, we hypothesized that c-Myc, SOX2, and Oct-4 expression would distinguish type II from type I FCDs. In addition, we assayed the expression of progenitor cell proteins forkhead box G1 (FOXG1), Kruppel-like factor 4 (KLF4), Nanog, and SOX3. Differential expression of 7 stem cellproteins and aberrant phosphorylation of2mTORC1 substrates, S6 andS6 kinase 1 proteins, clearly distinguished type II from type I FCDs(n = 10 each). Our results demonstrate new potential pathogenic pathways in type II FCDs and suggest biomarkers for diagnostic pathology in resected epilepsy specimens.
Figures




References
-
- Palmini A, Najm I, Avanzini G, et al. Terminology and classification of the cortical dysplasias. Neurology. 2004;62:S2–8. - PubMed
-
- Krsek P, Maton B, Korman B, et al. Different features of histopathological subtypes of pediatric focal cortical dysplasia. Ann Neurol. 2008;63:758–69. - PubMed
-
- Fauser S, Huppertz HJ, Bast T, et al. Clinical characteristics in focal cortical dysplasia: A retrospective evaluation in a series of 120 patients. Brain. 2006;129:1907–16. - PubMed
-
- Andre VM, Flores-Hernandez J, Cepeda C, et al. NMDA receptor alterations in neurons from pediatric cortical dysplasia tissue. Cereb Cortex. 2004;14:634–46. - PubMed
-
- Crino PB, Nathanson KL, Henske EP. The tuberous sclerosis complex. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1345–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

