Prophylactic intravenous indomethacin for preventing mortality and morbidity in preterm infants
- PMID: 20614421
- PMCID: PMC7045285
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000174.pub2
Prophylactic intravenous indomethacin for preventing mortality and morbidity in preterm infants
Abstract
Background: Persistent patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is associated with mortality and morbidity in preterm infants. Prostaglandin synthetase inhibitors such as indomethacin promote PDA closure but also have potential side effects. The effect of the prophylactic use of indomethacin, where infants who may not have gone on to develop a symptomatic PDA would be exposed to indomethacin, warrants particular scrutiny.
Objectives: To determine the effect of prophylactic indomethacin on mortality and morbidity in preterm infants.
Search strategy: The standard search strategy of the Cochrane Neonatal Review Group was used. This included searches of the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL, The Cochrane Library, Issue 5, 2010), MEDLINE, EMBASE and CINAHL (until April 2010), conference proceedings, and previous reviews.
Selection criteria: Randomised or quasi-randomised controlled trials that compared prophylactic indomethacin versus placebo or no drug in preterm infants.
Data collection and analysis: The standard methods of the Cochrane Neonatal Review Group were used, with separate evaluation of trial quality and data extraction by two review authors.
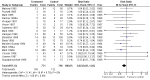
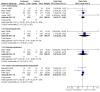
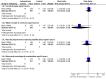
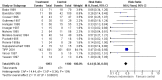
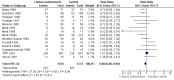
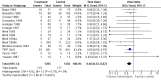
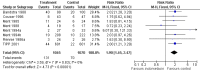
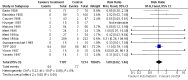
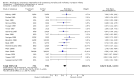
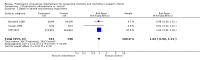
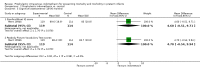
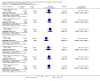
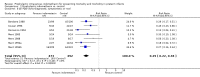
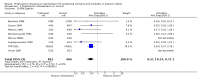
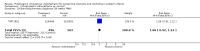
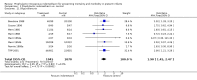
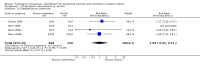
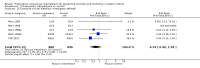
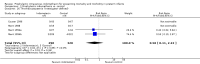
Main results: Nineteen eligible trials in which 2872 infants participated were identified. Most participants were very low birth weight, but the largest single trial restricted participation to extremely low birth weight infants (N = 1202). The trials were generally of good quality.The incidence of symptomatic PDA [typical relative risk (RR) 0.44, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.38 to 0.50] and PDA surgical ligation (typical RR 0.51, 95% CI 0.37,0.71) was significantly lower in treated infants. Prophylactic indomethacin also significantly reduced the incidence of severe intraventricular haemorrhage (typical RR 0.66, 95% CI 0.53 to 0.82). Meta-analyses found no evidence of an effect on mortality (typical RR 0.96, 95% CI 0.81 to 1.12) or on a composite of death or severe neurodevelopmental disability assessed at 18 to 36 months old (typical RR 1.02, 95% CI 0.90, 1.15).
Authors' conclusions: Prophylactic indomethacin has short-term benefits for preterm infants including a reduction in the incidence of symptomatic PDA, PDA surgical ligation, and severe intraventricular haemorrhage. However, there is no evidence of effect on mortality or neurodevelopment.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

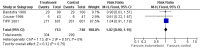





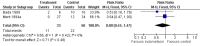
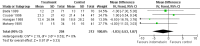


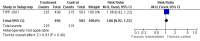
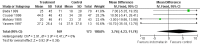

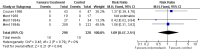
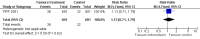



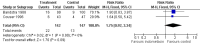

















Update of
-
Prophylactic intravenous indomethacin for preventing mortality and morbidity in preterm infants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(3):CD000174. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000174. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Jul 07;(7):CD000174. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000174.pub2. PMID: 12137607 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Bada 1989 {published data only}
-
- *Bada HS, Green RS, Pourcyrous M, et al. Indomethacin reduces the risks of severe intraventricular hemorrhage. Journal of Pediatrics 1989;115:631‐7. - PubMed
-
- Bada HS, Green RS, Pourcyrous M, Leffler CW, Korones SB, Arheart K. Indomethacin reduces relative risks of severe intraventricular hemorrhage [Abstract]. Pediatric Research 1989;25:353A. - PubMed
-
- Pourcyrous M, Bada HS, Green RS, Korones SB. Safety of indomethacin use for newborn infants [Abstract]. Pediatric Research 1988;23:422A.
Bandstra 1988 {published data only}
-
- *Bandstra ES, Montalvo BM, Goldberg RN, et al. Prophylactic indomethacin for prevention of intraventricular hemorrhage in premature infants. Pediatrics 1988;82:533‐542. - PubMed
-
- Bandstra ES, Bauer CR, Duenas ML, Chao H, Montalvo BM, Bancalari E. Prophylactic indomethacin for prevention of intraventricular hemorrhage: neurodevelopmental follow‐up [Abstract]. Annals of Neurology 1987;22:427A.
-
- Bandstra ES, Duenas ML, Rodriguez I, et al. Prophylactic indomethacin for the prevention of intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH): neurodevelopmental follow‐up [Abstract]. Pediatric Research 1987;21:391.
-
- Setzer ES, Morse BM, Goldberg RN, Smith M, Bancalari E. Prophylactic indomethacin and intraventricular hemorrhage in the premature [Abstract]. Pediatric Research 1984;18:345A.
-
- Setzer ES, Smith M, Goulding PJ, Bandstra TE. Severity of platelet dysfunction induced by prophylactic indomethacin in the premature [Abstract]. Pediatric Research 1984;18:346A.
Couser 1996 {published data only}
-
- *Couser RJ, Ferrara TB, Wright GB, Cabalka AK, Schilling CG, et al. Prophylactic indomethacin therapy in the first 24 hours of life for the prevention of patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants treated prophylactically with surfactant in the delivery room. Journal of Pediaitrcs 1996;128:631‐7. - PubMed
-
- Couser RJ, Hoekstra RE, Ferrara B, Wright GB, Cabalka AK, Connet JE. Neurodevelopmental follow‐up at 36 months' corrected age of preterm infants treated with prophylactic indomethacin. Archives of Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine 2000;154:598‐602. - PubMed
Domanico 1994 {published data only}
-
- Domanico RS, Waldman JD, Lester LA, McPhillips HA, Catrambone JE, Covert RF. Prophylactic indomethacin reduces the incidence of pulmonary hemorrhage and patent ductus arteriosus in surfactant‐treated infants < 1250 grams. Pediatric Research 1994;35:331A.
Gutierrez 1987 {published data only}
-
- Gutierrez NG, Lapasset M. Prophylactic indomethacin and the incidence of patent ductus arteriosus in preterm neonates. Proceedings of the 3rd Argentinian Congress of Perinatology, Buenos Aires. 1987; Vol. 62.
Hanigan 1988 {published data only}
-
- Hanigan WC, Kennedy G, Roemisch F, et al. Administration of indomethacin for the prevention of periventricular haemorrhage in high‐risk neonates. Journal of Pediatrics 1988;112:941‐7. - PubMed
Krueger 1987 {published data only}
-
- Krueger E, Mellander M, Bratton D, Cotton R. Prevention of symptomatic patent ductus arteriosus with a single dose of indomethacin. Journal of Pediatrics 1987;111:749‐54. - PubMed
Mahony 1985 {published data only}
-
- Mahony L, Caldwell RL, Girod DA, et al. Indomethacin therapy on the first day of life in infants with very low birth weight. Journal of Pediatrics 1985;106:801‐5. - PubMed
Ment 1985 {published data only}
-
- Ment LR, Duncan CC, Ehrenkranz RA, et al. Randomized indomethacin trial for prevention of intraventricular hemorrhage in very low birth weight infants. Journal of Pediatrics 1985;107:937‐43. - PubMed
Ment 1988 {published data only}
-
- Ment LR, Duncan CC, Ehrenkranz RA, et al. Randomized low‐dose indomethacin trial for prevention of intraventricular hemorrhage in very low birth weight neonates. Journal of Pediatrics 1988;112:948‐55. - PubMed
Ment 1994a {published data only}
-
- Ment LR, Oh W, Ehrenkranz, Phillip AGS, et al. Low‐dose indomethacin therapy and extension of intraventricular hemorrhage: a multicenter randomized trial. Journal of Pediatrics 1994;124:951‐5. - PubMed
Ment 1994b {published data only}
-
- Ment LR, Duncan CC, Ehrenkranz RA, Kleinman CS, Taylor KJW, Scott DT. Randomized low‐dose indomethacin trial for the prevention of intraventricular hemorrhage in very low birth weight neonates [Abstract]. Annals of Neurology 1987;22:406‐7.
-
- Ment LR, Oh W, Ehrenkranz RA, Phillip AG, Vohr B, Allan W, et al. Low‐dose indomethacin and prevention of intraventricular hemorrhage: a multicenter randomized trial. Pediatrics 1994;93:543‐50. - PubMed
-
- Ment LR, Vohr B, Allan W, Westerveld M, Sparrow SS, Schneider KC, et al. Outcome of children in the indomethacin intraventricular hemorrhage prevention trial. Pediatrics 2000;105:485‐91. - PubMed
-
- Ment LR, Vohr B, Oh W, Scott DT, Allen WC, Westerveld M, et al. Neurodevelopmental outcome at 36 months corrected age of preterm infants in the Multicenter Indomethacin Intraventricular Hemorrhage Prevention Trial. Pediatrics 1996;98:714‐8. - PubMed
Morales‐Suarez 1994 {published data only}
-
- Morales‐Suarez M, Lemus‐Varella L, Udaeta‐Mora E, Cardiel‐Marmolejo L, Rodriguez‐Balderrama I, Liz‐Cedilla RE. Indomethacin in the prevention of subependymal‐intraventricular hemorrhage in preterm newborns with conventional mechanical ventilation. Boletin Medico del Hospital Infantil de Mexico 1992;49:217‐24. - PubMed
-
- Morales‐Suarez M, Sanchez‐Gil T, Lemus‐Varela L. Low dose indomethacin for prevention of intraventricular hemorrhage in the preterm infant with mechanical ventilation: Final report of a randomized study [Estudio comparavito de dosis baja de indometacina profilactica para hemorragia subependimaria/intraventricular en neonatos pretermino con ventilation mecanica]. Boletin Medico del Hospital Infantil de Mexico 1994;51:389‐394.
Puckett 1985 {published data only}
-
- Puckett CG, Cox MA, Haskins KS, Fisher DJ. Prophylactic indomethacin (I) for the prevention of patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) [Abstract]. Pediatric Research 1985;19:358.
Rennie 1986a {published data only}
Supapannachart 1999 {published data only}
-
- Supapannachart S, Khowsathit P, Patchakapati B. Indomethacin prophylaxis for patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) in infants with a birth weight of less than 1250 grams. Journal of the Medical Associaition of Thailand 1999;82:S87‐S91. - PubMed
TIPP 2001 {published data only}
-
- Ohlsson A, Roberts RS, Schmidt B, Davis P, Moddeman D, Saigal S, et al. Male/female differences in indomethacin effects in preterm infants. Journal of Pediatrics 2005;147:860‐2. [PUBMED: 16356449] - PubMed
-
- Schmidt B, Davis P, Moddemann D, Ohlsson A, Roberts RS, Saigal S, et al. Long‐term effects of indomethacin prophylaxis in extremely‐low‐birth‐weight infants. New England Journal of Medicine 2001;344:1966‐72. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt B, Roberts RS, Fanaroff A, Davis P, Kirpalani HM, Nwaesei C, et al. Indomethacin prophylaxis, patent ductus arteriosus, and the risk of bronchopulmonary dysplasia: further analyses from the Trial of Indomethacin Prophylaxis in Preterms (TIPP). Journal of Pediatrics 2006;148:730‐4. - PubMed
-
- Zupancic JA, Richardson DK, O'Brien BJ, Cronin CG, Schmidt B, Roberts R, et al. Retrospective economic evaluation of a controlled trial of indomethacin prophylaxis for patent ductus arteriosus in premature infants. Early Human Development 2006;82:97‐103. - PubMed
Vincer 1987 {published data only}
-
- Vincer M, Allen A. Does prophylactic indomethacin in VLBW (<1500 grams birth weight) infants cause cerebral palsy (CP)?. Pediatric Research 1998;43:232.
-
- Vincer M, Allen A, Evans J, Nwaesei C, Stinson D, Rees E, et al. Early intravenous indomethacin prolongs respiratory support in very low birth weight infants. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica 1987;76:894‐7. - PubMed
Yaseen 1997 {published data only}
-
- Yaseen H, al Umran K, Ali H, Rustum M, Darwich M, al‐Faraidy A. Effects of early indomethacin administration on oxygenation and surfactant requirement in low birth weight infants. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 1997;43:42‐6. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Bada 1996 {published data only}
-
- Bada HS, Yolton KA, Duncan C, Wong SP, Pourcyrous M, Korones SB. Indomethacin (INDO) prophylaxis and outcome at school age [abstract]. Pediatric Research 1996;39:373A.
Cotton 1980 {published data only}
-
- Cotton RB, Hickey DE, Graham TP, Stahlman MT. Effects of early indomethacin (I) on ventilatory status of preterm infants with symptomatic patent ductus arteriosus (sPDA) [abstract]. Pediatric Research 1980;14:442A.
Cotton 1983 {published data only}
-
- Cotton L, Hickey D, Stahlman MT. Management of premature infants with symptomatic patent ductus arteriosus Intensive. In: Stern L editor(s). Care in the Newborn. IV. New York: Masson Publishing Co, 1983:225‐31.
Gersony 1983 {published data only}
-
- Gersony WM, Peckham GJ, Ellison RC, Miettinen OS, Nadas AS. Effects of indomethacin in premature infants with patent ductus arteriosus: results of a national collaborative study. Journal of Pediatrics 1983;102:895‐906. - PubMed
-
- Peckham GJ, Miettinen OS, Ellison RC, Kraybill EN, Gersony WM, Zeirler S, Nadas AS. Clinical course to 1 year if age in premature infants with patent ductus arteriosus: results of a multicenter randomized trial of indomethacin. Journal of Pediatrics 1984;104:285‐91. - PubMed
Hammerman 1986 {published data only}
-
- Hammerman C, Strates E, Valaitis S. The silent ductus: its precursors and its aftermath. Pediatric Cardiology 1986;7:121‐7. - PubMed
Hammerman 1987 {published data only}
-
- Hammerman C, Strates E, Komar K, Bui K. Failure of prophylactic indomethacin to improve the outcome of the very low birth weight infant. Developmental Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1987;10:393‐404. - PubMed
Hammerman 1990 {published data only}
-
- Hammerman C, Aramburo MJ. Prolonged indomethacin therapy for the prevention of recurrences of patent ductus arteriosus. Journal of Pediatrics 1990;117:771‐6. - PubMed
Hammerman 1995 {published data only}
-
- Hammerman C, Glaser J, Schimmel MS, Ferber B, Kaplan M, Eidelman AI. Continuous versus multiple rapid infusions of indomethacin: effects on cerebral blood flow velocity. Pediatrics 1995;95:244‐8. - PubMed
Kaapa 1983 {published data only}
-
- Kaapa P, Lanning P, Koivisto M. Early closure of patent ductus arteriosus with indomethacin in preterm infants with idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome. Acta Paediatrica Scandanavia 1983;72:179‐84. - PubMed
Krauss 1989 {published data only}
-
- Krauss AN, Fatica N, Lewis BS, Cooper R, Thaler HT, Cirrincione C, O'Loughlin J, Levin A, Engle MA, Auld PAM. Pulmonary function in preterm infants following treatment with intravenous indomethacin. American Journal of Diseases of Children 1989;143:78‐81. - PubMed
Lai 1990 {published data only}
-
- Lai TH, Soong WJ, Hwang B. Indomethacin for the prevention of symptomatic patent ductus arteriosus in very low birth weight infants. Acta Paediatrica Sinica 1990;31:17‐23. - PubMed
Mahony 1982 {published data only}
-
- *Mahony L, Carnero V, Brett C, Heymann MA, Clyman RI. Prophylactic indomethacin therapy for patent ductus arteriosus in very low birth weight infants. New England Journal of Medicine 1982;306:506‐10. - PubMed
-
- Mahony L, Heymann MA, Carnero V, Brett C, Clyman RI. When to treat the patent ductus arteriosus with indomethacin in very low birth weight infants. Advances in Prostaglandin, Thromboxane, and Leukotriene Research 1983;12:491‐4. - PubMed
Mardoum 1991 {published data only}
-
- Mardoum R, Bejar R, McFeely E, Peterson B, Merritt TA. Controlled study of the effects of indomethacin (INDO) on the cerebral blood flow velocities in the newborn infant [Abstract]. Pediatric Research 1988;23:554.
-
- Mardoum R, Bejar R, Merritt A, Berry C. Controlled study of the effects of indomethacin on cerebral blood flow velocities in newborn infants. Journal of Pediatrics 1991;118:112‐5. - PubMed
Ment 1987 {published data only}
-
- Ment LR, Duncan CC, Ehrenkranz RA, Kleinman CS, Taylor KJW, Scott DT. Randomized low‐dose indomethacin trial for the prevention of intraventricular hemorrhage in very low birth weight neonates [Abstract]. Annals of Neurology 1987;22:406‐7.
Ment 1993 {published data only}
-
- Ment LR, Oh W, Ehrenkrantz RA, Philip AGS, Schneider K, Katz KH, Taylor KJW, Duncan CC, Makuch. Risk period for intraventricular hemorrhage of the preterm neonate is independent of gestational age. Seminars in Perinatology 1993;17:338‐41. - PubMed
Merritt 1981 {published data only}
-
- Merritt TA, Harris JP, Roghmann K, Wood B, Campanella V, Alexzon C, Manning J, Shapiro DL. Early closure of patent ductus arteriosus in very low birth weight infants: a controlled trial. Journal of Pediatrics 1981;99:281‐6. - PubMed
Monset‐Couchard 1983 {published data only}
-
- Monset‐Couchard M, Dias‐Mancano D, Murat I, Relier JP. Controlled trial of intravenous lyophilized indomethacin in the treatment of persistent ductus arteriosus in premature infants [French]. Pediatrie 1983;38:365‐77. - PubMed
Mullett 1982 {published data only}
-
- *Mullett MD, Croghan TW, Myerberg DZ, Krall JM, Neal WA. Indomethacin closure of patent ductus arteriosus in prematures. Clinica Pediatrica 1982;21:217‐20. - PubMed
-
- Mullett MD, Crogan TW, Myerberg DZ, Neal WA. Administration of oral indomethacin (I) to prematures with patent ductus arteriosus (PDA): a randomized double blind study [Abstract]. Pediatric Research 1980;14:606.
Nestrud 1980 {published data only}
-
- Nestrud RM, Hill DE, Arrington RW, Beard AG, Dungan WT, Norton JB, Radinger RI. Indomethacin treatment in patent ductus arteriosus. A double blind study utilizing indomethacin plasma levels. Developmental Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1980;1:125‐36. - PubMed
Neu 1980 {published data only}
-
- Neu J, Ariagno RL, Johnson JD, Pitlick PT, Cohen JS, Beets CL. A double blind study of the effects of oral indomethacin (IN) in preterm infants with patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) who failed medical management [Abstract]. Pediatric Research 1980;14:607. - PubMed
Rennie 1991 {published data only}
Rhodes 1988 {published data only}
-
- Rhodes PG, Ferguson MG, Reddy NS, Joransen JA, Gibson J. Effects of prolonged versus acute indomethacin therapy in very low birth weight infants with patent ductus arteriosus. European Journal of Paediatrics 1988;147:481‐4. - PubMed
Rudd 1983 {published data only}
Valaes 1980 {published data only}
-
- Valaes T, Moylan FMB, Cohn H, Chung K, Nagpaul K, Chrenoff HL, Kreidberg MB. Incidence and significance of PDA in preterm infants (PTI) and controlled blind trial of indomethacin (IND) [Abstract]. Pediatric Research 1980;14:452.
van Overmeire 1995 {published data only}
-
- Overmeire B, Brus F, Acker KJ, et al. Aspirin versus indomethacin treatment of patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatric Research 1995;38:886‐91. - PubMed
Vogtmann 1988 {published data only}
-
- Vogtmann C, Grubbe G, Ruckhaberle KE, Bottcher H, Ockert C. Effects of early therapy with indomethacin on the manifestation of a persistent ductus arteriosus in extremely underweight premature infants [German]. Monatsschrift Kinderheilkunde 1988;136:636‐9. - PubMed
Wagner 1984 {published data only}
-
- Wagner HR, Ellison C, Zierler S, Lang P, Purohit DM, Behrendt D, Waldhausen JA. Surgical closure of patent ductus arteriosus in 268 preterm infants. Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery 1984;87:870‐5. - PubMed
Weesner 1987 {published data only}
-
- Weesner KM, Dillard RG, Boyle RJ, Block SM. Prophylactic treatment of asymptomatic ductus arteriosus in premature infants with respiratory distress syndrome. Southern Medical Journal 1987;80:706‐8. - PubMed
Wurtzel 1990 {published data only}
-
- Wurtzel D. Prenatal administration of indomethacin as a tocolytic agent: effect on neonatal renal function. Obstetrics and Gynecology 1990;76:689‐92. - PubMed
Yanagi 1981 {published data only}
-
- Yanagi RM, Wilson A, Newfeld EA, Aziz KU, Hubt CE. Indomethacin treatment for symptomatic patent ductus arteriosus: a double blind control study. Pediatrics 1981;67:647‐52. - PubMed
Yeh 1981 {published data only}
-
- *Yeh TF, Luken JA, Thalji A, Raval D, Carr I, Pildes RS. Intravenous indomethacin therapy in premature infants with persistent ductus arteriosus ‐ a double blind controlled study. Journal of Pediatrics 1981;98:137‐45. - PubMed
-
- Betkerur MV, Yeh TF, Miller K, Glasser RJ, Pildes RS. Indomethacin and its effect on renal function and urinary kallikrein excretion in premature infants with patent ductus arteriosus. Pediatrics 1981;68:99‐102. - PubMed
-
- Yeh TF, Goldbarg HR, Henek T, Thalji A, Pildes RS. Intravenous indomethacin therapy in premature infants with patent ductus arteriosus. Causes of death and one year follow‐up. American Journal of Diseases of Children 1982;136:803‐7. - PubMed
-
- Yeh TF, Raval D, Pyati S, Pildes RS. Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) and indomethacin therapy in premature infants with patent ductus arteriosus (PDA). Prostaglandins 1983;25:385‐91. - PubMed
-
- Yeh TF, Thalji A, Luken L, Lilien L, Carr I, Pildes RS. Improved lung compliance following indomethacin therapy in premature infants with patent ductus arteriosus. Chest 1981;80:698‐700. - PubMed
Zamboni 1993 {published data only}
-
- Zamboni G, Piemonte G, Boner A, et al. Influence of dietary taurine on vitamin D absorption. Acta Paediatrica 1993;82:811‐5. - PubMed
Additional references
Brown 1979
-
- Brown ER. Increased risk of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in infants with patent ductus arteriosus. Journal of Pediatrics 1979;95:865. - PubMed
Cifuentes 1979
-
- Cifuentes RF, Olley PM, Balfe JW, et al. Indomethacin and renal function in premature infants with persistent patent ductus arteriosus. Journal of Pediatrics 1979;95:583‐7. - PubMed
Cooke 2003
Coombs 1990
Edwards 1990
-
- Edwards AD, Wyatt JS, Richardson C, et al. Effects of indomethacin on cerebral haemodynamics in very preterm infants. Lancet 1990;335:1491‐5. - PubMed
Evans 1990
Evans 1995
Evans 1996
Fowlie 1996
Friedman 1978
-
- Friedman Z, Whitman V, Maisels MJ, et al. Indomethacin disposition and indomethacin‐induced platelet dysfunction in premature infants. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1978;18:272‐9. - PubMed
Herrera 2007
Heymann 1976
-
- Heymann MA, Rudolph AM, Silverman NH. Closure of the ductus arteriosus in premature infants by inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis. New England Journal of Medicine 1976;295:530‐3. - PubMed
ICROP 1984
-
- ICROP. An International Classification of Retinopathy of Prematurity. Pediatrics 1984;74:127‐133. - PubMed
Knight 2001
-
- Knight DB. The treatment of patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants. A review and overview of randomized trials. Seminars in Neonatology 2001;6:63‐73. - PubMed
Lipman 1982
-
- Lipman B, Server GA, Brazy JE. Abnormal cerebral haemodynamics in preterm infants with patent ductus arteriosus. Pediatrics 1982;69:778‐781. - PubMed
Malviya 2008
Mosalli 2008
Ohlsson 2008
Papile 1978
-
- Papile LA, Burstein J, Burstein R, Koffler H. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birthweights less than 1,500 grams. Journal of Pediatrics 1978;92:529‐34. - PubMed
Roberts 2009
-
- Roberts G, Doyle LW, Anderson PJ. The stability of the diagnosis of developmental disability between age 2 and 8 in a geographic cohort of very preterm children born In 1997. Archives of Disease in Childhood 2009;October 14:[Epub ahead of print]. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Fowlie 1997
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

