Near-infrared imaging of the sinuses: preliminary evaluation of a new technology for diagnosing maxillary sinusitis
- PMID: 20615013
- PMCID: PMC2887912
- DOI: 10.1117/1.3431718
Near-infrared imaging of the sinuses: preliminary evaluation of a new technology for diagnosing maxillary sinusitis
Abstract
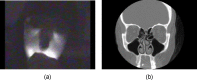
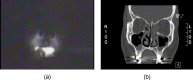
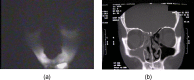
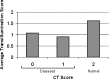
Diagnosing sinusitis remains a challenge for primary care physicians. There is a need for a simple, office-based technique to aid in the diagnosis of sinusitis without the cost and radiation risk of conventional radiologic imaging. We designed a low-cost near-infrared (NIR) device to transilluminate the maxillary sinuses. The use of NIR light allows for greater interrogation of deep-tissue structures as compared to visible light. NIR imaging of 21 patients was performed and compared with computed tomography (CT) scans. Individual maxillary sinuses were scored on a scale from 0 to 2 based on their degree of aeration present on CT and similarly based on the NIR signal penetration into the maxilla on NIR images. Our results showed that air-filled and fluid/tissue-filled spaces can be reasonably distinguished by their differing NIR signal penetration patterns, with average NIR imaging scores for fluid-filled maxillary sinuses (0.93+/-0.78, n=29) significantly lower than those for normal maxillary sinuses (1.62+/-0.57, n=13) (p=0.003). NIR imaging of the sinuses is a simple, safe, and cost-effective modality that can potentially aid in the diagnosis of sinusitis. Long-term, significant device refinement and large clinical trials will be needed to determine the diagnostic accuracy of this technique.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Near-Infrared Optical Imaging for Diagnosis of Maxillary Sinusitis.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016 Sep;155(3):538-41. doi: 10.1177/0194599816655309. Epub 2016 Jun 21. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016. PMID: 27329417
-
A Comparison of Near-Infrared Imaging and Computerized Tomography Scan for Detecting Maxillary Sinusitis.Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2022 Oct;131(10):1144-1150. doi: 10.1177/00034894211060623. Epub 2021 Nov 26. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2022. PMID: 34823368 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of static thermal and near-infrared hyperspectral imaging for the diagnosis of acute maxillary rhinosinusitis.J Otolaryngol. 2005 Apr;34(2):99-108. doi: 10.2310/7070.2005.04056. J Otolaryngol. 2005. PMID: 16076408
-
The silent sinus syndrome: a case series and literature review.Laryngoscope. 2001 Jun;111(6):975-8. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200106000-00008. Laryngoscope. 2001. PMID: 11404606 Review.
-
Imaging of Odontogenic Sinusitis.Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2024 Dec;57(6):1051-1067. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2024.06.010. Epub 2024 Aug 1. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2024. PMID: 39089984 Review.
Cited by
-
In vivo deep brain imaging of rats using oral-cavity illuminated photoacoustic computed tomography.J Biomed Opt. 2015 Jan;20(1):016019. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.20.1.016019. J Biomed Opt. 2015. PMID: 25611865 Free PMC article.
-
Rhinosinusitis in children.ISRN Otolaryngol. 2012 Dec 5;2012:851831. doi: 10.5402/2012/851831. Print 2012. ISRN Otolaryngol. 2012. PMID: 23762621 Free PMC article.
-
Monte Carlo modeling of light propagation in the human head for applications in sinus imaging.J Biomed Opt. 2015 Mar;20(3):035004. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.20.3.035004. J Biomed Opt. 2015. PMID: 25781310 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benninger M. S., Ferguson B. J., Hadley J. A., Hamilos D., Jacobs M., Kennedy D., Lanza D., Marple B., Osguthorpe J., and Stankiewicz J., “Adult chronic rhinosinusitis: definitions, diagnosis, epidemiology, and pathophysiology,” Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. OHNSDL 129, S1–32 (2003).10.1016/S0194-5998(03)01397-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Benson V. and Marano M. A., “Current estimates from the 1993 National Health Interview Survey,” National Center for Health Statistics, Vital Health Stat., 10, 190 (1994). - PubMed
-
- “National disease and therapeutic index,” pp. 487–488, IMS Health, Plymouth Meeting, PA (1988–1989).
-
- Stankiewicz J. A. and Chow J. M., “A diagnositic dilemma for chronic rhinosinusitis: definition accuracy and validity,” Am. J. Rhinol. ZZZZZZ 16, 199–202 (2002). - PubMed

