The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor PCI-32765 blocks B-cell activation and is efficacious in models of autoimmune disease and B-cell malignancy
- PMID: 20615965
- PMCID: PMC2919935
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1004594107
The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor PCI-32765 blocks B-cell activation and is efficacious in models of autoimmune disease and B-cell malignancy
Abstract
Activation of the B-cell antigen receptor (BCR) signaling pathway contributes to the initiation and maintenance of B-cell malignancies and autoimmune diseases. The Bruton tyrosine kinase (Btk) is specifically required for BCR signaling as demonstrated by human and mouse mutations that disrupt Btk function and prevent B-cell maturation at steps that require a functional BCR pathway. Herein we describe a selective and irreversible Btk inhibitor, PCI-32765, that is currently under clinical development in patients with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. We have used this inhibitor to investigate the biologic effects of Btk inhibition on mature B-cell function and the progression of B cell-associated diseases in vivo. PCI-32765 blocked BCR signaling in human peripheral B cells at concentrations that did not affect T cell receptor signaling. In mice with collagen-induced arthritis, orally administered PCI-32765 reduced the level of circulating autoantibodies and completely suppressed disease. PCI-32765 also inhibited autoantibody production and the development of kidney disease in the MRL-Fas(lpr) lupus model. Occupancy of the Btk active site by PCI-32765 was monitored in vitro and in vivo using a fluorescent affinity probe for Btk. Active site occupancy of Btk was tightly correlated with the blockade of BCR signaling and in vivo efficacy. Finally, PCI-32765 induced objective clinical responses in dogs with spontaneous B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. These findings support Btk inhibition as a therapeutic approach for the treatment of human diseases associated with activation of the BCR pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
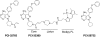
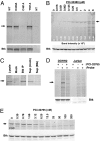
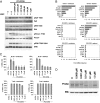
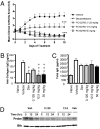

Comment in
-
Target discovery: Blocking BTK in B-cell disorders.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010 Sep;9(9):681. doi: 10.1038/nrd3262. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010. PMID: 20811379 No abstract available.
References
-
- Satterthwaite AB, Witte ON. The role of Bruton's tyrosine kinase in B-cell development and function: A genetic perspective. Immunol Rev. 2000;175:120–127. - PubMed
-
- Khan WN. Regulation of B lymphocyte development and activation by Bruton's tyrosine kinase. Immunol Res. 2001;23:147–156. - PubMed
-
- Humphries LA, et al. Tec kinases mediate sustained calcium influx via site-specific tyrosine phosphorylation of the phospholipase Cgamma Src homology 2-Src homology 3 linker. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:37651–37661. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

