Mutant superoxide dismutase 1-induced IL-1beta accelerates ALS pathogenesis
- PMID: 20616033
- PMCID: PMC2919927
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1002396107
Mutant superoxide dismutase 1-induced IL-1beta accelerates ALS pathogenesis
Abstract
ALS is a fatal motor neuron disease of adult onset. Neuroinflammation contributes to ALS disease progression; however, the inflammatory trigger remains unclear. We report that ALS-linked mutant superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) activates caspase-1 and IL-1beta in microglia. Cytoplasmic accumulation of mutant SOD1 was sensed by an ASC containing inflammasome and antagonized by autophagy, limiting caspase-1-mediated inflammation. Notably, mutant SOD1 induced IL-1beta correlated with amyloid-like misfolding and was independent of dismutase activity. Deficiency in caspase-1 or IL-1beta or treatment with recombinant IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA) extended the lifespan of G93A-SOD1 transgenic mice and attenuated inflammatory pathology. These findings identify microglial IL-1beta as a causative event of neuroinflammation and suggest IL-1 as a potential therapeutic target in ALS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
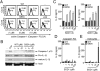


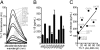

Comment in
-
Blocking IL-1beta to slow down progression of ALS?Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jul 20;107(29):12741-2. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1007946107. Epub 2010 Jul 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20624959 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

