LIM-domain proteins, LIMD1, Ajuba, and WTIP are required for microRNA-mediated gene silencing
- PMID: 20616046
- PMCID: PMC2906597
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0914987107
LIM-domain proteins, LIMD1, Ajuba, and WTIP are required for microRNA-mediated gene silencing
Abstract
In recent years there have been major advances with respect to the identification of the protein components and mechanisms of microRNA (miRNA) mediated silencing. However, the complete and precise repertoire of components and mechanism(s) of action remain to be fully elucidated. Herein we reveal the identification of a family of three LIM domain-containing proteins, LIMD1, Ajuba and WTIP (Ajuba LIM proteins) as novel mammalian processing body (P-body) components, which highlight a novel mechanism of miRNA-mediated gene silencing. Furthermore, we reveal that LIMD1, Ajuba, and WTIP bind to Ago1/2, RCK, Dcp2, and eIF4E in vivo, that they are required for miRNA-mediated, but not siRNA-mediated gene silencing and that all three proteins bind to the mRNA 5' m(7)GTP cap-protein complex. Mechanistically, we propose the Ajuba LIM proteins interact with the m(7)GTP cap structure via a specific interaction with eIF4E that prevents 4EBP1 and eIF4G interaction. In addition, these LIM-domain proteins facilitate miRNA-mediated gene silencing by acting as an essential molecular link between the translationally inhibited eIF4E-m(7)GTP-5(')cap and Ago1/2 within the miRISC complex attached to the 3'-UTR of mRNA, creating an inhibitory closed-loop complex.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
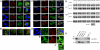
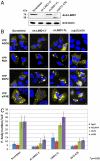
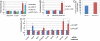
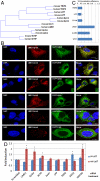
References
-
- Kato M, Slack FJ. microRNAs: Small molecules with big roles—C. elegans to human cancer. Biol Cell. 2008;100:71–81. - PubMed
-
- Valencia-Sanchez MA, Liu J, Hannon GJ, Parker R. Control of translation and mRNA degradation by miRNAs and siRNAs. Genes Dev. 2006;20:515–524. - PubMed
-
- Kadrmas JL, Beckerle MC. The LIM domain: From the cytoskeleton to the nucleus. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio. 2004;5:920–931. - PubMed
-
- Kumar MS, Lu J, Mercer KL, Golub TR, Jacks T. Impaired microRNA processing enhances cellular transformation and tumorigenesis. Nat Genet. 2007;39:673–677. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

