Mechanisms and implications of transcription blockage by guanine-rich DNA sequences
- PMID: 20616059
- PMCID: PMC2919923
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1007580107
Mechanisms and implications of transcription blockage by guanine-rich DNA sequences
Abstract
Various DNA sequences that interfere with transcription due to their unusual structural properties have been implicated in the regulation of gene expression and with genomic instability. An important example is sequences containing G-rich homopurine-homopyrimidine stretches, for which unusual transcriptional behavior is implicated in regulation of immunogenesis and in other processes such as genomic translocations and telomere function. To elucidate the mechanism of the effect of these sequences on transcription we have studied T7 RNA polymerase transcription of G-rich sequences in vitro. We have shown that these sequences produce significant transcription blockage in an orientation-, length- and supercoiling-dependent manner. Based upon the effects of various sequence modifications, solution conditions, and ribonucleotide substitutions, we conclude that transcription blockage is due to formation of unusually stable RNA/DNA hybrids, which could be further exacerbated by triplex formation. These structures are likely responsible for transcription-dependent replication blockage by G-rich sequences in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

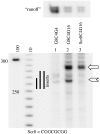
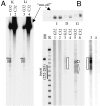
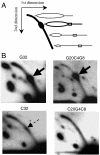
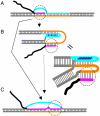
Similar articles
-
Transcription blockage by homopurine DNA sequences: role of sequence composition and single-strand breaks.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Feb 1;41(3):1817-28. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1333. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23275544 Free PMC article.
-
Strong transcription blockage mediated by R-loop formation within a G-rich homopurine-homopyrimidine sequence localized in the vicinity of the promoter.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jun 20;45(11):6589-6599. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx403. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28498974 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription blockage by stable H-DNA analogs in vitro.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Aug 18;43(14):6994-7004. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv622. Epub 2015 Jun 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26101261 Free PMC article.
-
PNA binding to the non-template DNA strand interferes with transcription, suggesting a blockage mechanism mediated by R-loop formation.Mol Carcinog. 2015 Nov;54(11):1508-12. doi: 10.1002/mc.22209. Epub 2014 Aug 30. Mol Carcinog. 2015. PMID: 25175074 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of T7 RNA polymerase transcription by phosphate and phosphorothioate triplex-forming oligonucleotides targeted to a R.Y site downstream from the promoter.Eur J Biochem. 1994 Dec 15;226(3):831-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.00831.x. Eur J Biochem. 1994. PMID: 7813472
Cited by
-
The Role of Long Non-coding RNAs in Human Imprinting Disorders: Prospective Therapeutic Targets.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 25;9:730014. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.730014. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34760887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-B DNA: a major contributor to small- and large-scale variation in nucleotide substitution frequencies across the genome.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Feb 22;49(3):1497-1516. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa1269. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33450015 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive nutraceuticals as G4 stabilizers: potential cancer prevention and therapy-a critical review.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Jun;397(6):3585-3616. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02857-z. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38019298 Review.
-
Dynamic alternative DNA structures in biology and disease.Nat Rev Genet. 2023 Apr;24(4):211-234. doi: 10.1038/s41576-022-00539-9. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Nat Rev Genet. 2023. PMID: 36316397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TERRA regulates DNA G-quadruplex formation and ATRX recruitment to chromatin.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Nov 28;50(21):12217-12234. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1114. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 36440760 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hanawalt PC. Transcription-coupled repair and human disease. Science. 1994;266:1957–1958. - PubMed
-
- Mirkin SM. DNA structures, repeat expansions and human hereditary disorders. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2006;16:351–358. - PubMed
-
- Wang G, Vasquez KM. Non-B DNA structure-induced genetic instability. Mutat Res. 2006;598:103–119. - PubMed
-
- Bacolla A, Wells RD. Non-B DNA conformations as determinants of mutagenesis and human disease. Mol Carcinog. 2009;48:273–285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

