Mechanisms and implications of transcription blockage by guanine-rich DNA sequences
- PMID: 20616059
- PMCID: PMC2919923
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1007580107
Mechanisms and implications of transcription blockage by guanine-rich DNA sequences
Abstract
Various DNA sequences that interfere with transcription due to their unusual structural properties have been implicated in the regulation of gene expression and with genomic instability. An important example is sequences containing G-rich homopurine-homopyrimidine stretches, for which unusual transcriptional behavior is implicated in regulation of immunogenesis and in other processes such as genomic translocations and telomere function. To elucidate the mechanism of the effect of these sequences on transcription we have studied T7 RNA polymerase transcription of G-rich sequences in vitro. We have shown that these sequences produce significant transcription blockage in an orientation-, length- and supercoiling-dependent manner. Based upon the effects of various sequence modifications, solution conditions, and ribonucleotide substitutions, we conclude that transcription blockage is due to formation of unusually stable RNA/DNA hybrids, which could be further exacerbated by triplex formation. These structures are likely responsible for transcription-dependent replication blockage by G-rich sequences in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

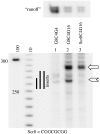
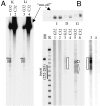
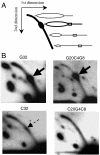
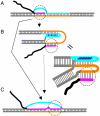
References
-
- Hanawalt PC. Transcription-coupled repair and human disease. Science. 1994;266:1957–1958. - PubMed
-
- Mirkin SM. DNA structures, repeat expansions and human hereditary disorders. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2006;16:351–358. - PubMed
-
- Wang G, Vasquez KM. Non-B DNA structure-induced genetic instability. Mutat Res. 2006;598:103–119. - PubMed
-
- Bacolla A, Wells RD. Non-B DNA conformations as determinants of mutagenesis and human disease. Mol Carcinog. 2009;48:273–285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

