SHIP2, a factor associated with diet-induced obesity and insulin sensitivity, attenuates FGF signaling in vivo
- PMID: 20616095
- PMCID: PMC2965400
- DOI: 10.1242/dmm.000703
SHIP2, a factor associated with diet-induced obesity and insulin sensitivity, attenuates FGF signaling in vivo
Abstract
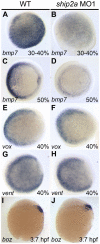
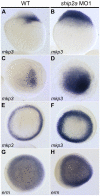
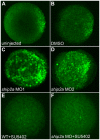
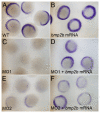
SH2-domain-containing inositol phosphatase 2 (SHIP2) belongs to a small family of phosphoinositide 5-phosphatases that help terminate intracellular signaling initiated by activated receptor tyrosine kinases. Mammalian SHIP2 is viewed primarily as an attenuator of insulin signaling and has become a prominent candidate target for therapeutic agents that are designed to augment insulin signaling. Despite this view, no signaling pathway has yet been demonstrated as being affected directly by SHIP2 function in vivo, and in vitro studies indicate that the protein may function in multiple signaling pathways. Here, we analyze the role of a SHIP2 family member in the early zebrafish embryo where developmental and gene expression defects can be used to assay specific signaling pathways. The zebrafish ship2a transcript is maternally supplied, and inhibiting the expression of its protein product results in the expansion of dorsal tissue fates at the expense of ventral ones. We show that the developmental defects are the result of perturbation of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signaling in the early embryo. Loss of Ship2a leads to an increased and expanded expression of outputs of FGF-mediated signaling, including FGF-dependent gene expression and activated mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling. Our findings demonstrate that Ship2a attenuates the FGF signaling pathway in vivo and functions in the establishment of normal tissue patterning in the early embryo. We suggest that modulation of FGF signaling may be a principal function of SHIP2 in mammals.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dual role of SRC homology domain 2-containing inositol phosphatase 2 in the regulation of platelet-derived growth factor and insulin-like growth factor I signaling in rat vascular smooth muscle cells.Endocrinology. 2003 Sep;144(9):4204-14. doi: 10.1210/en.2003-0190. Endocrinology. 2003. PMID: 12933696
-
Zebrafish endoderm formation is regulated by combinatorial Nodal, FGF and BMP signalling.Development. 2006 Jun;133(11):2189-200. doi: 10.1242/dev.02387. Epub 2006 May 3. Development. 2006. PMID: 16672336
-
Piwi-like 2 mediates fibroblast growth factor signaling during gastrulation of zebrafish embryo.Tohoku J Exp Med. 2010 Sep;222(1):63-8. doi: 10.1620/tjem.222.63. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2010. PMID: 20814180
-
Lipid phosphatases as a possible therapeutic target in cases of type 2 diabetes and obesity.Pharmacol Ther. 2006 Dec;112(3):799-809. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2006.06.001. Epub 2006 Jul 13. Pharmacol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16842857 Review.
-
The SH2 domain containing inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase-2: SHIP2.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005 Nov;37(11):2260-5. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2005.05.003. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15964236 Review.
Cited by
-
INPPL1 gene mutations in opsismodysplasia.J Hum Genet. 2017 Feb;62(2):135-140. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2016.119. Epub 2016 Oct 6. J Hum Genet. 2017. PMID: 27708270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 screens reveal shared and cell-specific mechanisms of resistance to SHP2 inhibition.J Exp Med. 2023 May 1;220(5):e20221563. doi: 10.1084/jem.20221563. Epub 2023 Feb 23. J Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 36820830 Free PMC article.
-
The ventral to dorsal BMP activity gradient in the early zebrafish embryo is determined by graded expression of BMP ligands.Dev Biol. 2013 Jun 15;378(2):170-82. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.03.003. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23499658 Free PMC article.
-
The SH2-domain-containing inositol 5-phosphatase (SHIP) limits the motility of neutrophils and their recruitment to wounds in zebrafish.J Cell Sci. 2012 Nov 1;125(Pt 21):4973-8. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106625. Epub 2012 Sep 3. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 22946052 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Suppressor Lzap Suppresses Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling to Promote Zebrafish Embryonic Ventral Cell Fates via the Suppression of Inhibitory Phosphorylation of Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3.J Biol Chem. 2015 Dec 11;290(50):29808-19. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.669309. Epub 2015 Oct 16. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26475862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Affolter M, Basler K. (2007). The Decapentaplegic morphogen gradient: from pattern formation to growth regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 8, 663–674 - PubMed
-
- Artemenko Y, Gagnon A, Sorisky A. (2009). Catalytically inactive SHIP2 inhibits proliferation by attenuating PDGF signaling in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J Cell Physiol. 218, 228–236 - PubMed
-
- Backers K, Blero D, Paternotte N, Zhang J, Erneux C. (2003). The termination of PI3K signalling by SHIP1 and SHIP2 inositol 5-phosphatases. Adv Enzyme Regul. 43, 15–28 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

