Naturally occurring human urinary peptides for use in diagnosis of chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 20616184
- PMCID: PMC2984241
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M110.001917
Naturally occurring human urinary peptides for use in diagnosis of chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Because of its availability, ease of collection, and correlation with physiology and pathology, urine is an attractive source for clinical proteomics/peptidomics. However, the lack of comparable data sets from large cohorts has greatly hindered the development of clinical proteomics. Here, we report the establishment of a reproducible, high resolution method for peptidome analysis of naturally occurring human urinary peptides and proteins, ranging from 800 to 17,000 Da, using samples from 3,600 individuals analyzed by capillary electrophoresis coupled to MS. All processed data were deposited in an Structured Query Language (SQL) database. This database currently contains 5,010 relevant unique urinary peptides that serve as a pool of potential classifiers for diagnosis and monitoring of various diseases. As an example, by using this source of information, we were able to define urinary peptide biomarkers for chronic kidney diseases, allowing diagnosis of these diseases with high accuracy. Application of the chronic kidney disease-specific biomarker set to an independent test cohort in the subsequent replication phase resulted in 85.5% sensitivity and 100% specificity. These results indicate the potential usefulness of capillary electrophoresis coupled to MS for clinical applications in the analysis of naturally occurring urinary peptides.
Figures

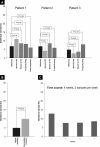
References
-
- Alebiosu C. O., Ayodele O. E. (2005) The global burden of chronic kidney disease and the way forward. Ethn. Dis. 15, 418–423 - PubMed
-
- Good D. M., Thongboonkerd V., Novak J., Bascands J. L., Schanstra J. P., Coon J. J., Dominiczak A., Mischak H. (2007) Body fluid proteomics for biomarker discovery: lessons from the past hold the key to success in the future. J. Proteome Res. 6, 4549–4555 - PubMed
-
- Kolch W., Neusüss C., Pelzing M., Mischak H. (2005) Capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry as a powerful tool in clinical diagnosis and biomarker discovery. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 24, 959–977 - PubMed
-
- González-Buitrago J. M., Ferreira L., Lorenzo I. (2007) Urinary proteomics. Clin. Chim. Acta 375, 49–56 - PubMed
-
- Fliser D., Novak J., Thongboonkerd V., Argilés A., Jankowski V., Girolami M. A., Jankowski J., Mischak H. (2007) Advances in urinary proteome analysis and biomarker discovery. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 18, 1057–1071 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK082753/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK075868/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK080301/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK080301/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK078244/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RG/02/012/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- T32 GM008349/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 29240/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R56 DK078244/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK075868/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK067638/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G0401466/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- DK061525/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK082753/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK078244/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK061525/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK067638/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32GM08349/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK041526/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

