The oxygen tension modulates acetaminophen-induced mitochondrial oxidant stress and cell injury in cultured hepatocytes
- PMID: 20616211
- PMCID: PMC2940407
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq208
The oxygen tension modulates acetaminophen-induced mitochondrial oxidant stress and cell injury in cultured hepatocytes
Abstract
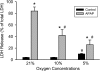
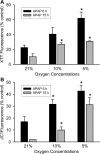
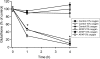
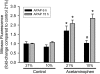
Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction play an important role in acetaminophen (APAP)-induced hepatocyte cell death. However, exact mechanisms involved in the process are controversial, in part, because of the disparity in findings between in vitro and in vivo studies. A major difference in this context is the oxygen tension, with cells in culture being exposed to 21% oxygen, whereas those in the liver experience a gradient from 3 to 9% oxygen. To determine if oxygen tensions could modulate hepatocyte responses to APAP, primary mouse hepatocytes were treated with 5mM APAP for up to 15 h under various oxygen tensions and mitochondrial dysfunction (2,3-bis[2-methoxy-4-nitro-5-sulfophenyl]-2H-tetrazolium-5-carboxyanilide inner salt assay, 5,5',6,6'-tetrachloro-1,1,3,3-tetraethylbenzimidazolylcarbocyanine iodide [JC-1] fluorescence ratio) and cell death (lactate dehydrogenase release) was evaluated. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen species were measured using Mitosox Red or dihydrorhodamine fluorescence and nitrotyrosine staining, respectively. Exposure of hepatocytes to 5mM APAP at 21% O(2) resulted in mitochondrial oxidant stress formation, deterioration of mitochondrial function, and loss of membrane potential as early as 6 h and massive cell death at 15 h. Culture of cells at 10% O(2) resulted in no increase in mitochondrial oxidant stress and better preserved mitochondrial function at 6 h and significant protection against cell death at 15 h. Furthermore, dihydrorhodamine fluorescence was significantly attenuated at 10% oxygen. Cells cultured at 5% oxygen were also protected but showed evidence of hypoxia (accumulation of lactate and nuclear translocation of hypoxia-inducing factor-1α). These results suggest that oxygen tension can modulate hepatocyte responses to APAP, with low physiological levels (10%) decreasing mitochondrial oxidant stress and delaying hepatocyte cell death.
Figures




References
-
- Albano E, Poli G, Chiarpotto E, Biasi F, Dianzani MU. Paracetamol-stimulated lipid peroxidation in isolated rat and mouse hepatocytes. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1983;47:249–263. - PubMed
-
- Bajt ML, Cover C, Lemasters JJ, Jaeschke H. Nuclear translocation of endonuclease G and apoptosis-inducing factor during acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Toxicol. Sci. 2006;94:217–225. - PubMed
-
- Bajt ML, Farhood A, Lemasters JJ, Jaeschke H. Mitochondrial bax translocation accelerates DNA fragmentation and cell necrosis in a murine model of acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008;324:8–14. - PubMed
-
- Bajt ML, Knight TR, Farhood A, Jaeschke H. Scavenging peroxynitrite with glutathione promotes regeneration and enhances survival during acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003;307:67–73. - PubMed
-
- Bajt ML, Knight TR, Lemasters JJ, Jaeschke H. Acetaminophen-induced oxidant stress and cell injury in cultured mouse hepatocytes: protection by N-acetyl cysteine. Toxicol. Sci. 2004;80:343–349. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

