A B2 SINE insertion in the Comt1 gene (Comt1(B2i)) results in an overexpressing, behavior modifying allele present in classical inbred mouse strains
- PMID: 20618449
- PMCID: PMC3037563
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2010.00614.x
A B2 SINE insertion in the Comt1 gene (Comt1(B2i)) results in an overexpressing, behavior modifying allele present in classical inbred mouse strains
Abstract
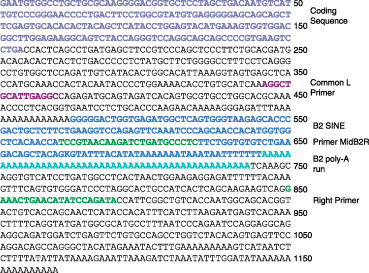
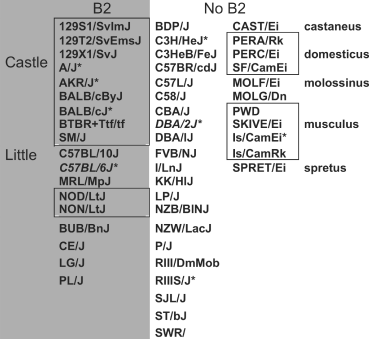
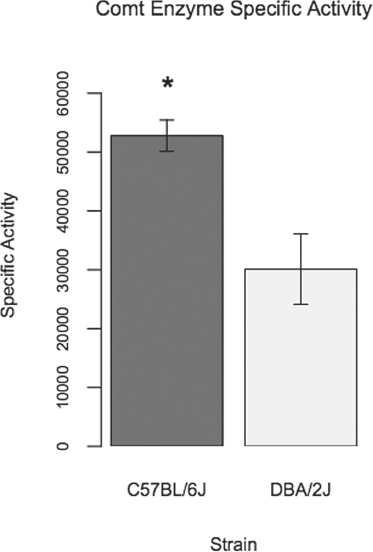
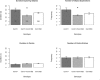
Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) is a key enzyme for dopamine catabolism and COMT is a candidate gene for human psychiatric disorders. In mouse it is located on chromosome 16 in a large genomic region of extremely low variation among the classical inbred strains, with no confirmed single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between strains C57BL/6J and DBA/2J within a 600-kB window. We found a B2 SINE in the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of Comt1 which is present in C57BL/6J (Comt1(B2i)) and other strains including 129 (multiple sublines), but is not found in DBA/2J (Comt1(+)) and many other strains including wild-derived Mus domesticus, M. musculus, M. molossinus, M.castaneus and M. spretus. Comt1(B2i) is absent in strains closely related to C57BL/6, such as C57L and C57BR, indicating that it was polymorphic in the cross that gave rise to these strains. The strain distribution of Comt1(B2i) indicates a likely origin of the allele in the parental Lathrop stock. A stringent association test, using 670 highly outbred mice (Boulder Heterogeneous Stock), indicates that this insertion allele may be responsible for a difference in behavior related to exploration. Gene expression differences at the mRNA and enzyme activity level (1.7-fold relative to wild type) indicate a mechanism for this behavioral effect. Taken together, these findings show that Comt1(B2i) (a B2 SINE insertion) results in a relatively modest difference in Comt1 expression and enzyme activity (comparable to the human Val-Met polymorphism) which has a demonstrable behavioral phenotype across a variety of outbred genetic backgrounds.
© 2010 The Authors. Genes, Brain and Behavior © 2010 Blackwell Publishing Ltd and International Behavioural and Neural Genetics Society.
Figures
References
-
- Babovic D, O'Tuathaigh CM, O'Sullivan GJ, Clifford JJ, Tighe O, Croke DT, Karayiorgou M, Gogos JA, Cotter D, Waddington JL. Exploratory and habituation phenotype of heterozygous and homozygous COMT knockout mice. Behav Brain Res. 2007;183:236–239. - PubMed
-
- Beck JA, Lloyd S, Hafezparast M, Lennon-Pierce M, Eppig JT, Festing MFW, Fisher EMC. Genealogies of mouse inbred strains. Nat Genet. 2000;24:23–25. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Lipska BK, Halim N, Ma QD, Matsumoto M, Melhem S, Kolachana BS, Hyde TM, Herman MM, Apud J, Egan MF, Kleinman JE, Weinberger DR. Functional analysis of genetic variation in catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT): effects on mrna, protein, and enzyme activity in postmortem human brain. Am J Hum Genet. 2004;75:807–821. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chernova T, Higginson FM, Davies R, Smith AG. B2 SINE retrotransposon causes polymorphic expression of mouse 5-aminolevulinic acid synthase 1 gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;377:515–520. - PubMed
-
- Chia R, Achilli F, Festing MF, Fisher EM. The origins and uses of mouse outbred stocks. Nat Genet. 2005;37:1181–1186. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

