Epigenetic organization of brain sex differences and juvenile social play behavior
- PMID: 20619265
- PMCID: PMC3015020
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2010.06.017
Epigenetic organization of brain sex differences and juvenile social play behavior
Abstract
The study of epigenetic mechanisms is important for elucidating how gene-by-environment interactions can have lasting outcomes on brain function and behavior. In general, studies of epigenetic processes mainly focus on the methylation status of DNA. While methylation of DNA alone can interfere with gene transcription, it is the binding of methyl-CpG binding proteins to methylated DNA, and subsequent recruitment of nuclear corepressors and histone deacetylases, that results in more efficient gene repression. In this review, we will discuss sex differences in DNA methylation patterns, methyl binding proteins, and corepressor proteins that contribute to lasting differences in brain and juvenile behavior. Specifically, we will discuss new data on sex differences in ERα DNA promoter methylation patterns, and the role of MeCP2 and the nuclear corepressor, NCoR, on the organization of juvenile social play behavior.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
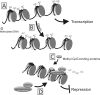

References
-
- Alland L, Muhle R, Hou H, Jr., Potes J, Chin L, Schreiber-Agus N, DePinho RA. Role for N-CoR and histone deacetylase in Sin3-mediated transcriptional repression. Nature. 1997;387:49–55. - PubMed
-
- Amir RE, Van den Veyver IB, Wan M, Tran CQ, Francke U, Zoghbi HY. Rett syndrome is caused by mutations in X-linked MECP2, encoding methyl-CpG-binding protein 2. Nat. Genet. 1999;23:185–188. - PubMed
-
- Baum MJ. Differentiation of coital behavior in mammals: a comparative analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1979;3:265–284. - PubMed
-
- Beatty WW, Dodge AM, Traylor KL, Meaney MJ. Temporal boundary of the sensitive period for hormonal organization of social play in juvenile rats. Physiol Behav. 1981;26:241–243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

