Macrophages and immunologic inflammation of the kidney
- PMID: 20620669
- PMCID: PMC2922007
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2010.03.003
Macrophages and immunologic inflammation of the kidney
Abstract
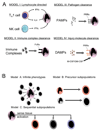
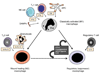
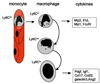
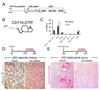
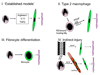
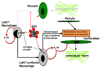
Monocyte-derived tissue effector cells, macrophages, are present in large numbers in all forms of kidney disease with inflammation. Their roles in inflammation and the molecular effectors of macrophage function have been difficult to decipher. With the advent of modern genetic tools and mouse models of human disease, great insight into monocyte/macrophage biology has been forthcoming. This review places macrophage study in its historical context, defines immunologic diseases of the kidney, broadens its definition to encompass current thinking of the immune response to kidney injury, highlights key advances of the study of monocyte/macrophages in kidney diseases, and identifies new therapeutic pathways and targets that hinge around macrophage function. This article advances the case that targeting macrophage activation and phenotype is leading to new therapies in the treatment of many acute and chronic kidney diseases.
Figures

References
-
- van Furth R. Macrophage activity and clinical immunology. Origin and kinetics of mononuclear phagocytes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;278:161–175. - PubMed
-
- Magil AB, Wadsworth LD. Monocyte involvement in glomerular crescents: a histochemical and ultrastructural study. Lab Invest. 1982;47(2):160–166. - PubMed
-
- Germain MJ, Anderson RW, Keane WF. Renal disease in cryoglobulinemia type II: response to therapy. A case report and review of the literature. Am J Nephrol. 1982;2(4):221–226. - PubMed
-
- Ferrario F, Castiglione A, Colasanti G, et al. The detection of monocytes in human glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1985;28(3):513–519. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

