Discrete roles of STAT4 and STAT6 transcription factors in tuning epigenetic modifications and transcription during T helper cell differentiation
- PMID: 20620946
- PMCID: PMC2904651
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.06.003
Discrete roles of STAT4 and STAT6 transcription factors in tuning epigenetic modifications and transcription during T helper cell differentiation
Abstract
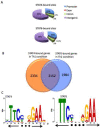
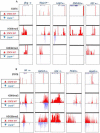
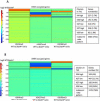
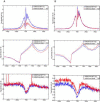
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 4 (STAT4) and STAT6 are key factors in the specification of helper T cells; however, their direct roles in driving differentiation are not well understood. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation and massive parallel sequencing, we quantitated the full complement of STAT-bound genes, concurrently assessing global STAT-dependent epigenetic modifications and gene transcription by using cells from cognate STAT-deficient mice. STAT4 and STAT6 each bound over 4000 genes with distinct binding motifs. Both played critical roles in maintaining chromatin configuration and transcription of a core subset of genes through the combination of different epigenetic patterns. Globally, STAT4 had a more dominant role in promoting active epigenetic marks, whereas STAT6 had a more prominent role in antagonizing repressive marks. Clusters of genes negatively regulated by STATs were also identified, highlighting previously unappreciated repressive roles of STATs. Therefore, STAT4 and STAT6 play wide regulatory roles in T helper cell specification.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Abbas AK, Murphy KM, Sher A. Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature. 1996;383:787–793. - PubMed
-
- Afkarian M, Sedy JR, Yang J, Jacobson NG, Cereb N, Yang SY, Murphy TL, Murphy KM. T-bet is a STAT1-induced regulator of IL-12R expression in naive CD4+ T cells. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:549–557. - PubMed
-
- Ansel KM, Djuretic I, Tanasa B, Rao A. Regulation of Th2 differentiation and Il4 locus accessibility. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:607–656. - PubMed
-
- Bailey TL, Elkan C. Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. Proc Int Conf Intell Syst Mol Biol. 1994;2:28–36. - PubMed
-
- Beima KM, Miazgowicz MM, Lewis MD, Yan PS, Huang TH, Weinmann AS. T-bet binding to newly identified target gene promoters is cell type-independent but results in variable context-dependent functional effects. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:11992–12000. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

