miR-200c regulates induction of apoptosis through CD95 by targeting FAP-1
- PMID: 20620960
- PMCID: PMC2904349
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.05.018
miR-200c regulates induction of apoptosis through CD95 by targeting FAP-1
Abstract
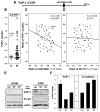
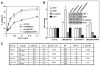
Tumor progression shares many characteristics with the process of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Cells that have undergone an EMT are known to have an increased resistance to apoptosis. CD95/Fas is an apoptosis-inducing receptor expressed on many tissues and tumor cells. During tumor progression CD95 is frequently downregulated, and tumor cells lose apoptosis sensitivity. miR-200 microRNAs repress both the EMT-inducing ZEB1 and ZEB2 transcription factors. We now demonstrate that miR-200c sensitizes cells to apoptosis mediated by CD95. We have identified the apoptosis inhibitor FAP-1 as a target for miR-200c. FAP-1 was demonstrated to be responsible for the reduced sensitivity to CD95-mediated apoptosis in cells with inhibited miR-200. The identification of FAP-1 as an miR-200c target provides a molecular mechanism to explain both the downregulation of CD95 expression and the reduction in sensitivity of cells to CD95-mediated apoptosis that is observed in the context of reduced miR-200 expression during tumor progression.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Elnemr A, Ohta T, Yachie A, Kayahara M, Kitagawa H, Fujimura T, Ninomiya I, Fushida S, Nishimura GI, Shimizu K, Miwa K. Human pancreatic cancer cells disable function of Fas receptors at several levels in Fas signal transduction pathway. Int J Oncol. 2001;18:311–316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

