Transcriptomic analyses of xylan degradation by Prevotella bryantii and insights into energy acquisition by xylanolytic bacteroidetes
- PMID: 20622018
- PMCID: PMC2943253
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.141788
Transcriptomic analyses of xylan degradation by Prevotella bryantii and insights into energy acquisition by xylanolytic bacteroidetes
Abstract
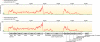
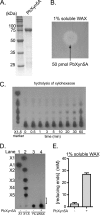
Enzymatic depolymerization of lignocellulose by microbes in the bovine rumen and the human colon is critical to gut health and function within the host. Prevotella bryantii B(1)4 is a rumen bacterium that efficiently degrades soluble xylan. To identify the genes harnessed by this bacterium to degrade xylan, the transcriptomes of P. bryantii cultured on either wheat arabinoxylan or a mixture of its monosaccharide components were compared by DNA microarray and RNA sequencing approaches. The most highly induced genes formed a cluster that contained putative outer membrane proteins analogous to the starch utilization system identified in the prominent human gut symbiont Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. The arrangement of genes in the cluster was highly conserved in other xylanolytic Bacteroidetes, suggesting that the mechanism employed by xylan utilizers in this phylum is conserved. A number of genes encoding proteins with unassigned function were also induced on wheat arabinoxylan. Among these proteins, a hypothetical protein with low similarity to glycoside hydrolases was shown to possess endoxylanase activity and subsequently assigned to glycoside hydrolase family 5. The enzyme was designated PbXyn5A. Two of the most similar proteins to PbXyn5A were hypothetical proteins from human colonic Bacteroides spp., and when expressed each protein exhibited endoxylanase activity. By using site-directed mutagenesis, we identified two amino acid residues that likely serve as the catalytic acid/base and nucleophile as in other GH5 proteins. This study therefore provides insights into capture of energy by xylanolytic Bacteroidetes and the application of their enzymes as a resource in the biofuel industry.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

