Apelin attenuates hyperoxic lung and heart injury in neonatal rats
- PMID: 20622042
- PMCID: PMC3001263
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200909-1361OC
Apelin attenuates hyperoxic lung and heart injury in neonatal rats
Abstract
Rationale: Apelin, a potent vasodilator and angiogenic factor, may be a novel therapeutic agent in neonatal chronic lung disease, including bronchopulmonary dysplasia.
Objectives: To determine the beneficial effect of apelin in neonatal rats with hyperoxia-induced lung injury, a model for premature infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia.
Methods: The cardiopulmonary effects of apelin treatment (62 μg/kg/d) were studied in neonatal rats by exposure to 100% oxygen, using two treatment strategies: early concurrent treatment during continuous exposure to hyperoxia for 10 days and late treatment and recovery in which treatment was started on Day 6 after hyperoxic injury for 9 days and continued during the 9-day recovery period. We investigated in both models the role of the nitric oxide-cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) pathway in apelin treatment by specific inhibition of the nitric oxide synthase activity with N(ω)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME, 25 mg/kg/d).
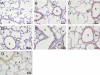
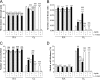
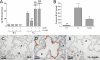
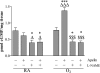
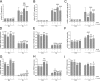
Measurements and main results: Parameters investigated include survival, lung and heart histopathology, pulmonary fibrin deposition and inflammation, alveolar vascular leakage, lung cGMP levels, right ventricular hypertrophy, and differential mRNA expression in lung and heart tissue. Prophylactic treatment with apelin improved alveolarization and angiogenesis, increased lung cGMP levels, and reduced pulmonary fibrin deposition, inflammation, septum thickness, arteriolar wall thickness, and right ventricular hypertrophy. These beneficial effects were completely absent in the presence of L-NAME. In the injury-recovery model apelin also improved alveolarization and angiogenesis, reduced arteriolar wall thickness, and attenuated right ventricular hypertrophy.
Conclusions: Apelin reduces pulmonary inflammation, fibrin deposition, and right ventricular hypertrophy, and partially restores alveolarization in rat pups with neonatal hyperoxic lung injury via a nitric oxide synthase-dependent mechanism.
Figures
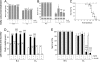

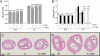
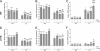
Similar articles
-
Sildenafil attenuates pulmonary inflammation and fibrin deposition, mortality and right ventricular hypertrophy in neonatal hyperoxic lung injury.Respir Res. 2009 Apr 29;10(1):30. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-10-30. Respir Res. 2009. PMID: 19402887 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibition attenuates persistent heart and lung injury by neonatal hyperoxia in rats.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012 Jan 1;302(1):L56-67. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00041.2011. Epub 2011 Sep 23. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012. PMID: 21949154 Free PMC article.
-
Agonists of MAS oncogene and angiotensin II type 2 receptors attenuate cardiopulmonary disease in rats with neonatal hyperoxia-induced lung injury.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2013 Sep;305(5):L341-51. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00360.2012. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23812633 Free PMC article.
-
Ambrisentan reduces pulmonary arterial hypertension but does not stimulate alveolar and vascular development in neonatal rats with hyperoxic lung injury.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2013 Feb 15;304(4):L264-75. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00073.2012. Epub 2013 Jan 4. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23292811 Free PMC article.
-
Supplemental Oxygen in the Newborn: Historical Perspective and Current Trends.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Nov 25;10(12):1879. doi: 10.3390/antiox10121879. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34942982 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Apelin retards the progression of diabetic nephropathy.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2013 Mar 15;304(6):F788-800. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00306.2012. Epub 2013 Jan 9. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23303408 Free PMC article.
-
Single cell transcriptomic analysis of murine lung development on hyperoxia-induced damage.Nat Commun. 2021 Mar 10;12(1):1565. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21865-2. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33692365 Free PMC article.
-
Apelin as a new therapeutic target for COVID-19 treatment.QJM. 2023 Mar 27;116(3):197-204. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcac229. QJM. 2023. PMID: 36200913 Free PMC article.
-
Perinatal Hyperoxia and Developmental Consequences on the Lung-Brain Axis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Feb 24;2022:5784146. doi: 10.1155/2022/5784146. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35251477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Infects Enteric Neurons and Triggers Gut Dysfunction via Macrophage Recruitment.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Mar 15;8:74. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00074. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29600197 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baraldi E, Filippone M. Chronic lung disease after premature birth. N Engl J Med 2007;357:1946–1955. - PubMed
-
- Jobe AH, Bancalari E. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001;163:1723–1729. - PubMed
-
- Jobe AJ. The new BPD: an arrest of lung development. Pediatr Res 1999;46:641–643. - PubMed
-
- Kinsella JP, Greenough A, Abman SH. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Lancet 2006;367:1421–1431. - PubMed
-
- Warner BB, Stuart LA, Papes RA, Wispe JR. Functional and pathological effects of prolonged hyperoxia in neonatal mice. Am J Physiol 1998;275:L110–L117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

