Dual two-component regulatory systems are involved in aromatic compound degradation in a polychlorinated-biphenyl degrader, Rhodococcus jostii RHA1
- PMID: 20622058
- PMCID: PMC2937422
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00429-10
Dual two-component regulatory systems are involved in aromatic compound degradation in a polychlorinated-biphenyl degrader, Rhodococcus jostii RHA1
Abstract
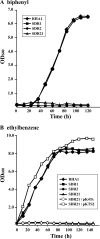
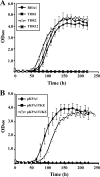
A Gram-positive polychlorinated-biphenyl (PCB) degrader, Rhodococcus jostii RHA1, degrades PCBs by cometabolism with biphenyl. A two-component BphS1T1 system encoded by bphS1 and bphT1 (formerly bphS and bphT) is responsible for the transcription induction of the five gene clusters, bphAaAbAcAdC1B1, etbAa1Ab1CbphD1, etbAa2Ab2AcD2, etbAdbphB2, and etbD1, which constitute multiple enzyme systems for biphenyl/PCB degradation. The bphS2 and bphT2 genes, which encode BphS2 and BphT2, virtually identical to BphS1 (92%) and BphT1 (97%), respectively, were characterized. BphS2T2 induced the activation of the bphAa promoter in a host, Rhodococcus erythropolis IAM1399, in the presence of a variety of aromatics, including benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, xylenes, isopropylbenzene, and chlorinated benzenes, as effectively as BphS1T1. The substrate spectrum of BphS2T2 was the same as that of BphS1T1, except for biphenyl, which is a substrate only for BphS1T1. BphS2T2 activated transcription from the five promoters of biphenyl/PCB degradation enzyme gene clusters as effectively as BphS1T1. The targeted disruptions of the bphS1, bphS2, bphT1, and bphT2 genes indicated that all these genes are involved in the growth of RHA1 on aromatic compounds. The hybrid system with bphS1 and bphT2 and that with bphS2 and bphT1 were constructed, and both systems conducted induced activation of the bphAa promoter, indicating cross-communication. These results indicated that RHA1 employs not only multiple enzyme systems, but also dual regulatory systems for biphenyl/PCB degradation. Comparison of the sequences, including bphS2T2, with the bphS1T1-containing sequences and the corresponding sequences in other rhodococcal degraders suggests that bphS2T2 might have originated from bphS1T1.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The 24-bp consensus sequence responsible for regulation of the BphS1T1 two-component system in a hybrid promoter.J Biosci Bioeng. 2012 Mar;113(3):279-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2011.10.021. Epub 2011 Dec 1. J Biosci Bioeng. 2012. PMID: 22133760
-
Gene cluster and regulation system for 1,1-dichloro-2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethylene (DDE) degradation in Janibacter sp. TYM3221.J Biosci Bioeng. 2013 Jul;116(1):91-100. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2013.01.007. Epub 2013 Feb 13. J Biosci Bioeng. 2013. PMID: 23415487
-
Multiple-subunit genes of the aromatic-ring-hydroxylating dioxygenase play an active role in biphenyl and polychlorinated biphenyl degradation in Rhodococcus sp. strain RHA1.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006 Aug;72(8):5396-402. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00298-06. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16885291 Free PMC article.
-
Adventures in Rhodococcus - from steroids to explosives.Can J Microbiol. 2011 Mar;57(3):155-68. doi: 10.1139/W10-115. Can J Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21358756 Review.
-
[PCB degradation systems in Rhodococcus bacteria: multiplex enzyme system determined by multiple isozyme genes].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2005 Oct;50(12):1541-7. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2005. PMID: 16218454 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Functional characterization of diverse ring-hydroxylating oxygenases and induction of complex aromatic catabolic gene clusters in Sphingobium sp. PNB.FEBS Open Bio. 2014 Mar 7;4:290-300. doi: 10.1016/j.fob.2014.03.001. eCollection 2014. FEBS Open Bio. 2014. PMID: 24918041 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Regulation of the Peripheral Pathway for the Anaerobic Catabolism of Toluene and m-Xylene in Azoarcus sp. CIB.Front Microbiol. 2018 Mar 22;9:506. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00506. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29623071 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effect of monoterpenes and flavonoids on the transcription of aromatic ring-hydroxylating dioxygenase genes in Rhodococcus opacus C1 and Rhodococcus sp. WAY2.Microb Genom. 2025 Mar;11(3):001359. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.001359. Microb Genom. 2025. PMID: 40042991 Free PMC article.
-
Genome Sequencing and Comparative Transcriptomics Provide a Holistic View of 4-Nitrophenol Degradation and Concurrent Fatty Acid Catabolism by Rhodococcus sp. Strain BUPNP1.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jan 4;9:3209. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.03209. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30662435 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial degradation of benzoate: cross-regulation between aerobic and anaerobic pathways.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 23;287(13):10494-10508. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.309005. Epub 2012 Feb 2. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22303008 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmad, D., R. Massé, and M. Sylvestre. 1990. Cloning and expression of genes involved in 4-chlorobiphenyl transformation by Pseudomonas testosteroni: homology to polychlorobiphenyl-degrading genes in other bacteria. Gene 86:53-61. - PubMed
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. - PubMed
-
- Bijlsma, J. J., and E. A. Groisman. 2003. Making informed decisions: regulatory interactions between two-component systems. Trends. Microbiol. 11:359-366. - PubMed
-
- Choi, E. N., M. C. Cho, Y. Kim, C. K. Kim, and K. Lee. 2003. Expansion of growth substrate range in Pseudomonas putida F1 by mutations in both cymR and todS, which recruit a ring-fission hydrolase CmtE and induce the tod catabolic operon, respectively. Microbiology 149:795-805. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

