Functional identification of the Proteus mirabilis core lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis genes
- PMID: 20622068
- PMCID: PMC2937370
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00494-10
Functional identification of the Proteus mirabilis core lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis genes
Abstract
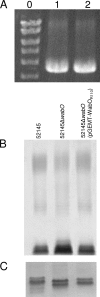
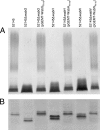
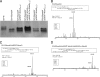
In this study, we report the identification of genes required for the biosynthesis of the core lipopolysaccharides (LPSs) of two strains of Proteus mirabilis. Since P. mirabilis and Klebsiella pneumoniae share a core LPS carbohydrate backbone extending up to the second outer-core residue, the functions of the common P. mirabilis genes was elucidated by genetic complementation studies using well-defined mutants of K. pneumoniae. The functions of strain-specific outer-core genes were identified by using as surrogate acceptors LPSs from two well-defined K. pneumoniae core LPS mutants. This approach allowed the identification of two new heptosyltransferases (WamA and WamC), a galactosyltransferase (WamB), and an N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (WamD). In both strains, most of these genes were found in the so-called waa gene cluster, although one common core biosynthetic gene (wabO) was found outside this cluster.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Genomic and proteomic studies on Plesiomonas shigelloides lipopolysaccharide core biosynthesis.J Bacteriol. 2014 Feb;196(3):556-67. doi: 10.1128/JB.01100-13. Epub 2013 Nov 15. J Bacteriol. 2014. PMID: 24244003 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic characterization of the Klebsiella pneumoniae waa gene cluster, involved in core lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis.J Bacteriol. 2001 Jun;183(12):3564-73. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.12.3564-3573.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11371519 Free PMC article.
-
The inner-core lipopolysaccharide biosynthetic waaE gene: function and genetic distribution among some Enterobacteriaceae.Microbiology (Reading). 2002 Nov;148(Pt 11):3485-3496. doi: 10.1099/00221287-148-11-3485. Microbiology (Reading). 2002. PMID: 12427940
-
Functional identification of Proteus mirabilis eptC gene encoding a core lipopolysaccharide phosphoethanolamine transferase.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Apr 21;15(4):6689-702. doi: 10.3390/ijms15046689. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24756091 Free PMC article.
-
Proteus mirabilis and Klebsiella pneumoniae as pathogens capable of causing co-infections and exhibiting similarities in their virulence factors.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Oct 20;12:991657. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.991657. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36339335 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Three enzymatic steps required for the galactosamine incorporation into core lipopolysaccharide.J Biol Chem. 2010 Dec 17;285(51):39739-49. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.168385. Epub 2010 Oct 19. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20959463 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the hidden arsenal: new insights into Proteus mirabilis virulence in UTIs.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Nov 13;14:1465460. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1465460. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39606746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipopolysaccharide structure modulates cationic biocide susceptibility and crystalline biofilm formation in Proteus mirabilis.Front Microbiol. 2023 Apr 5;14:1150625. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1150625. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37089543 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic and proteomic studies on Plesiomonas shigelloides lipopolysaccharide core biosynthesis.J Bacteriol. 2014 Feb;196(3):556-67. doi: 10.1128/JB.01100-13. Epub 2013 Nov 15. J Bacteriol. 2014. PMID: 24244003 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of carbohydrates and glycoconjugates by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry: an update for 2009-2010.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2015 May-Jun;34(3):268-422. doi: 10.1002/mas.21411. Epub 2014 May 26. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2015. PMID: 24863367 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Belas, R. 1996. Proteus mirabilis swarmer cell differentiation and urinary tract infection, p. 271-298. In H. L. T. Mobley and J. W. Warren (ed.), Urinary tract infections: molecular pathogenesis and clinical management. ASM Press, Washington, DC.
-
- Belunis, C. J., T. Clementz, S. M. Carty, and C. H. R. Raetz. 1995. Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis and cell growth following inactivation of the kdtA gene of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 270:27646-27652. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

