Kinetics of contraction-induced GLUT4 translocation in skeletal muscle fibers from living mice
- PMID: 20622170
- PMCID: PMC2927934
- DOI: 10.2337/db10-0233
Kinetics of contraction-induced GLUT4 translocation in skeletal muscle fibers from living mice
Abstract
Objective: Exercise is an important strategy for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. This is due in part to an increase in glucose transport that occurs in the working skeletal muscles. Glucose transport is regulated by GLUT4 translocation in muscle, but the molecular machinery mediating this process is poorly understood. The purpose of this study was to 1) use a novel imaging system to elucidate the kinetics of contraction-induced GLUT4 translocation in skeletal muscle and 2) determine the function of AMP-activated protein kinase alpha2 (AMPKalpha2) in this process.
Research design and methods: Confocal imaging was used to visualize GLUT4-enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) in transfected quadriceps muscle fibers in living mice subjected to contractions or the AMPK-activator AICAR.
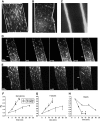
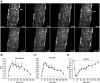
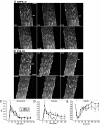
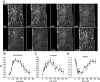
Results: Contraction increased GLUT4-EGFP translocation from intracellular vesicle depots to both the sarcolemma and t-tubules with similar kinetics, although translocation was greater with contractions elicited by higher voltage. Re-internalization of GLUT4 did not begin until 10 min after contractions ceased and was not complete until 130 min after contractions. AICAR increased GLUT4-EGFP translocation to both sarcolemma and t-tubules with similar kinetics. Ablation of AMPKalpha2 activity in AMPKalpha2 inactive transgenic mice did not change GLUT4-EGFP's basal localization, contraction-stimulated intracellular GLUT4-EGFP vesicle depletion, translocation, or re-internalization, but diminished AICAR-induced translocation.
Conclusions: We have developed a novel imaging system to study contraction-stimulated GLUT4 translocation in living mice. Contractions increase GLUT4 translocation to the sarcolemma and t-tubules with similar kinetics and do not require AMPKalpha2 activity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Large GLUT4 vesicles are stationary while locally and reversibly depleted during transient insulin stimulation of skeletal muscle of living mice: imaging analysis of GLUT4-enhanced green fluorescent protein vesicle dynamics.Diabetes. 2008 Feb;57(2):315-24. doi: 10.2337/db06-1578. Epub 2007 Oct 31. Diabetes. 2008. PMID: 17977960
-
Electroporated GLUT4-7myc-GFP detects in vivo glucose transporter 4 translocation in skeletal muscle without discernible changes in GFP patterns.Exp Physiol. 2019 May;104(5):704-714. doi: 10.1113/EP087545. Epub 2019 Mar 14. Exp Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30710396
-
Gene gun bombardment-mediated expression and translocation of EGFP-tagged GLUT4 in skeletal muscle fibres in vivo.Pflugers Arch. 2002 Sep;444(6):710-21. doi: 10.1007/s00424-002-0862-5. Epub 2002 Jul 27. Pflugers Arch. 2002. PMID: 12355170
-
In vivo imaging of GLUT4 translocation.Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2009 Jun;34(3):420-3. doi: 10.1139/H09-043. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2009. PMID: 19448708 Review.
-
Insulin- and contraction-induced glucose transporter 4 traffic in muscle: insights from a novel imaging approach.Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2013 Apr;41(2):77-86. doi: 10.1097/JES.0b013e318275574c. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2013. PMID: 23072821 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Measurements of basal d-glucose transport through GLUT1 across the intact plasma membrane of isolated segments from single fast- and slow-twitch skeletal muscle fibres of rat.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2022 Apr;234(4):e13789. doi: 10.1111/apha.13789. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2022. PMID: 35038771 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between rectus abdominis muscle thickness and metabolic syndrome in middle-aged men.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 15;12(9):e0185040. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185040. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28915276 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Neuronal nitric oxide synthase mediates insulin- and oxidative stress-induced glucose uptake in skeletal muscle myotubes.Free Radic Biol Med. 2017 Sep;110:261-269. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.06.018. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 28666850 Free PMC article.
-
Musclin Is Related to Insulin Resistance and Body Composition, but Not to Body Mass Index or Cardiorespiratory Capacity in Adults.Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2021 Oct;36(5):1055-1068. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2021.1104. Epub 2021 Oct 21. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2021. PMID: 34674511 Free PMC article.
-
CFTR Deficiency Affects Glucose Homeostasis via Regulating GLUT4 Plasma Membrane Transportation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Feb 15;9:630654. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.630654. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33659254 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marette A, Burdett E, Douen A, Vranic M, Klip A. Insulin induces the translocation of GLUT4 from a unique intracellular organelle to transverse tubules in rat skeletal muscle. Diabetes 1992;41:1562–1569 - PubMed
-
- Lauritzen HP, Ploug T, Prats C, Tavaré JM, Galbo H. Imaging of insulin signaling in skeletal muscle of living mice shows major role of t-tubules. Diabetes 2006;55:1300–1306 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

