Genome-wide association study identifies a sequence variant within the DAB2IP gene conferring susceptibility to abdominal aortic aneurysm
- PMID: 20622881
- PMCID: PMC4157066
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.622
Genome-wide association study identifies a sequence variant within the DAB2IP gene conferring susceptibility to abdominal aortic aneurysm
Abstract
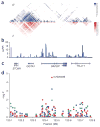
We performed a genome-wide association study on 1,292 individuals with abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) and 30,503 controls from Iceland and The Netherlands, with a follow-up of top markers in up to 3,267 individuals with AAAs and 7,451 controls. The A allele of rs7025486 on 9q33 was found to associate with AAA, with an odds ratio (OR) of 1.21 and P = 4.6 x 10(-10). In tests for association with other vascular diseases, we found that rs7025486[A] is associated with early onset myocardial infarction (OR = 1.18, P = 3.1 x 10(-5)), peripheral arterial disease (OR = 1.14, P = 3.9 x 10(-5)) and pulmonary embolism (OR = 1.20, P = 0.00030), but not with intracranial aneurysm or ischemic stroke. No association was observed between rs7025486[A] and common risk factors for arterial and venous diseases-that is, smoking, lipid levels, obesity, type 2 diabetes and hypertension. Rs7025486 is located within DAB2IP, which encodes an inhibitor of cell growth and survival.
Figures
References
-
- Crawford CM, Hurtgen-Grace K, Talarico E, Marley J. Abdominal aortic aneurysm: an illustrated narrative review. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2003;26:184–195. - PubMed
-
- Grootenboer N, Bosch JL, Hendriks JM, van Sambeek MR. Epidemiology, aetiology, risk of rupture and treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysms: does sex matter? Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2009;38:278–284. - PubMed
-
- Assar AN, Zarins CK. Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm: a surgical emergency with many clinical presentations. Postgrad Med J. 2009;85:268–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

