Measurement of the normal lumbar intervertebral disc space using magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 20622948
- PMCID: PMC2900163
- DOI: 10.4184/asj.2010.4.1.1
Measurement of the normal lumbar intervertebral disc space using magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
Study design: This is a retrospective study.
Purpose: We wanted to measure the distance of the normal intervetebral disc space of Koreans. OVERVIEW OF THE LITERATURE: For judging the distance of the normal intervertebral disc space of Koreans, we studied young adults who didn't have degenerative spinal change to determine the distance of the normal intervertebral disc space of each lumbar vertebral segment, and we did so by performing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Methods: We studied a total of 178 outpatients who had low back pain and they underwent lumbar MRI. There were 138 males and 40 females, and their average age was 20.7 years (range, 15 to 25 years). On MRI, the segments with observed Modic change or other abnormalities were excluded from this investigation. To improvement the accuracy of measurement, two spine specialists measured the distances 2 times, and we calculated the mean value. We used paired t-tests for statistical analysis.
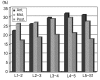
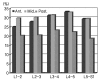
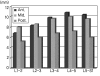
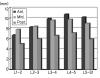
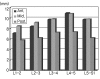
Results: In the total 178 patients, the average distance of intervertebral space from the 1st to the 2nd lumbar vertebrae was 24.83% (range, 18 to 32%), that from the 2nd to the 3rd was 26.92% (range, 19 to 40%), that from the 3rd to 4th was 28.88% (range, 19 to 41%), that from the 4th to 5th was 29.60% (range, 21 to 43%) and that from the 5th lumbar vertebra to the 1st sacrum was 27.52% (range, 19 to 38%).
Conclusions: In this study, we expect that knowing the normal distance of the lumbar intervertebral space of Koreans can be helpful for surgical reconstruction to treat many lumbar spine diseases, to predict the appropriate size of the devices inserted in the intervertebral space and to produce proper devices for Koreans.
Keywords: Lumbar intervertebral disc; Magnetic resonance imaging; Measurement.
Figures


References
-
- Haughton VM. MR imaging of the spine. Radiology. 1988;166:297–301. - PubMed
-
- Masaryk TJ, Ross JS, Modic MT, Boumphrey F, Bohlman H, Wilber G. High-resolution MR imaging of sequestered lumbar intervertebral disks. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1988;150:1155–1162. - PubMed
-
- Modic MT, Pavlicek W, Weinstein MA, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of intervertebral disk disease: clinical and pulse sequence considerations. Radiology. 1984;152:103–111. - PubMed
-
- Marnay T. Lumbar disc replacement: 7-11 year results with Prodisc. Eur Spine J. 2002;11:19.
-
- Bertagnoli R, Yue JJ, Kershaw T, et al. Lumbar total disc arthroplasty utilizing the ProDisc prosthesis in smokers versus nonsmokers: a prospective study with 2-year minimum follow-up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2006;31:992–997. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

