Circulating microRNA in body fluid: a new potential biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis
- PMID: 20624164
- PMCID: PMC11159200
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01650.x
Circulating microRNA in body fluid: a new potential biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis
Abstract
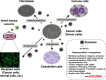
In the past several years, the importance of microRNA (miRNA) in cancer cells has been recognized. Proper control of miRNA expression is essential for maintaining a steady state of the cellular machinery. Recently, it was discovered that extracellular miRNAs circulate in the blood of both healthy and diseased patients, although ribonuclease is present in both plasma and serum. Most of the circulating miRNAs are included in lipid or lipoprotein complexes, such as apoptotic bodies, microvesicles, or exosomes, and are, therefore, highly stable. The existence of circulating miRNAs in the blood of cancer patients has raised the possibility that miRNAs may serve as a novel diagnostic marker. However, the secretory mechanism and biological function, as well as the meaning of the existence of extracellular miRNAs, remain largely unclear. In this review, we summarize the usefulness of circulating miRNA for cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutics. Furthermore, we propose a mechanism for the secretion and incorporation of miRNA into the cells.
© 2010 Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures

References
-
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin‐4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin‐14. Cell 1993; 75: 843–54. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004; 116: 281–97. - PubMed
-
- Kim VN, Han J, Siomi MC. Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2009; 10: 126–39. - PubMed
-
- Rosenfeld N, Aharonov R, Meiri E et al. MicroRNAs accurately identify cancer tissue origin. Nat Biotechnol 2008; 26: 462–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

