Arsenic antagonizes the Hedgehog pathway by preventing ciliary accumulation and reducing stability of the Gli2 transcriptional effector
- PMID: 20624968
- PMCID: PMC2922148
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1006822107
Arsenic antagonizes the Hedgehog pathway by preventing ciliary accumulation and reducing stability of the Gli2 transcriptional effector
Abstract
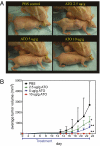
Aberrant Hedgehog (Hh) pathway activation has been implicated in cancers of diverse tissues and organs, and the tumor growth-inhibiting effects of pathway antagonists in animal models have stimulated efforts to develop pathway antagonists for human therapeutic purposes. These efforts have focused largely on cyclopamine derivatives or other compounds that mimic cyclopamine action in binding to and antagonizing Smoothened, a membrane transductory component. We report here that arsenicals, in contrast, antagonize the Hh pathway by targeting Gli transcriptional effectors; in the short term, arsenic blocks Hh-induced ciliary accumulation of Gli2, the primary activator of Hh-dependent transcription, and with prolonged incubation arsenic reduces steady-state levels of Gli2. Arsenicals active in Hh pathway antagonism include arsenic trioxide (ATO), a curative agent in clinical use for acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL); in our studies, ATO inhibited growth of Hh pathway-driven medulloblastoma allografts derived from Ptch+/-p53-/- mice within a range of serum levels comparable to those achieved in treatment of human APL. Arsenic thus could be tested rapidly as a therapeutic agent in malignant diseases associated with Hh pathway activation and could be particularly useful in such diseases that are inherently resistant or have acquired resistance to cyclopamine mimics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chiang C, et al. Cyclopia and defective axial patterning in mice lacking Sonic hedgehog gene function. Nature. 1996;383:407–413. - PubMed
-
- Jessell TM. Neuronal specification in the spinal cord: Inductive signals and transcriptional codes. Nat Rev Genet. 2000;1:20–29. - PubMed
-
- Ingham PW, McMahon AP. Hedgehog signaling in animal development: Paradigms and principles. Genes Dev. 2001;15:3059–3087. - PubMed
-
- Varjosalo M, Taipale J. Hedgehog: Functions and mechanisms. Genes Dev. 2008;22:2454–2472. - PubMed
-
- Teglund S, Toftgård R. Hedgehog beyond medulloblastoma and basal cell carcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1805:181–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

