Angiotensin II type 1 receptor-mediated augmentation of urinary excretion of endogenous angiotensin II in Val5-angiotensin II-infused rats
- PMID: 20625079
- PMCID: PMC4038977
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.153106
Angiotensin II type 1 receptor-mediated augmentation of urinary excretion of endogenous angiotensin II in Val5-angiotensin II-infused rats
Abstract
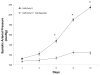
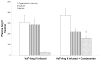
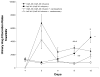
Rats infused chronically with Val(5)-Angiotensin (Ang) II exhibit increased urinary excretion of endogenous Ile(5)-Ang II by the 12th day of infusion, suggesting the stimulation of endogenous Ang II formation by Val(5)-Ang II infusion. The present study determined the time course of increased urinary Ang II excretion and the effects of Ang II type 1 receptor blockade (candesartan, 2 mg/kg per day) on the urinary excretion rates of Ile(5)-Ang II in Val(5)-Ang II-infused (80 ng/min) rats. Ile(5)-Ang II was separated from Val(5)-Ang II by high-performance liquid chromatography and measured by radioimmunoassay. Systolic blood pressure increased progressively (215+/-2 mm Hg) in Val(5)-Ang II-infused rats (n=5), whereas the candesartan-treated group (n=6) remained normotensive (124+/-3 mm Hg). Candesartan treatment significantly increased the level of plasma Ile(5)-Ang II (24.0+/-7.6 versus 156.9+/-24.6 fmol/mL; P<0.01); in contrast, there was a markedly lower intrarenal Ile(5)-Ang II content (357.9+/-76.6 versus 21.1+/-2.8 fmol/g; P<0.01). Urinary Ile(5)-Ang II excretion rates were elevated by day 9 (2185.7+/-283.2 fmol/24 hours) in Val(5)-Ang II-infused rats but not in candesartan-treated rats (740.6+/-110.3 fmol/24 hours). Thus, Ang II type 1 receptor blockade prevents the increase in urinary excretion of endogenous Ang II in rats subjected to chronic Ang II infusion. These data indicate that the increased urinary excretion of endogenous Ang II in Val(5)-Ang II-infused rats is primarily attributed to Ang II type 1 receptor-dependent secretion into and/or de novo formation of Ang II within the tubular lumen.
Figures

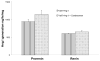

Comment in
-
On the origin of urinary angiotensin II.Hypertension. 2010 Oct;56(4):e45; author reply e46. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.159798. Epub 2010 Aug 23. Hypertension. 2010. PMID: 20733083 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Augmentation of endogenous intrarenal angiotensin II levels in Val5-ANG II-infused rats.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009 May;296(5):F1067-71. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.90596.2008. Epub 2009 Feb 25. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19244403 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II type 1 receptor-mediated augmentation of renal interstitial fluid angiotensin II in angiotensin II-induced hypertension.J Hypertens. 2003 Oct;21(10):1897-903. doi: 10.1097/00004872-200310000-00017. J Hypertens. 2003. PMID: 14508196
-
Increased renin excretion is associated with augmented urinary angiotensin II levels in chronic angiotensin II-infused hypertensive rats.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011 Dec;301(6):F1195-201. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00339.2011. Epub 2011 Aug 24. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21865264 Free PMC article.
-
Renal responses to AT1 receptor blockade.Am J Hypertens. 2000 Jan;13(1 Pt 2):45S-54S. doi: 10.1016/s0895-7061(99)00248-4. Am J Hypertens. 2000. PMID: 10678288 Review.
-
Regulation of intrarenal angiotensin II in hypertension.Hypertension. 2002 Feb;39(2 Pt 2):316-22. doi: 10.1161/hy0202.103821. Hypertension. 2002. PMID: 11882566 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor does not suppress renal angiotensin II levels in angiotensin I-infused rats.J Pharmacol Sci. 2013;122(2):103-8. doi: 10.1254/jphs.13045fp. Epub 2013 May 22. J Pharmacol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23698111 Free PMC article.
-
Hormone-Dependent Regulation of Renin and Effects on Prorenin Receptor Signaling in the Collecting Duct.Curr Hypertens Rev. 2022;18(2):91-100. doi: 10.2174/1573402118666220216105357. Curr Hypertens Rev. 2022. PMID: 35170417 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II stimulates renin in inner medullary collecting duct cells via protein kinase C and independent of epithelial sodium channel and mineralocorticoid receptor activity.Hypertension. 2011 Mar;57(3):594-9. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.165902. Epub 2011 Jan 31. Hypertension. 2011. PMID: 21282553 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II increases the expression of (pro)renin receptor during low-salt conditions.Am J Med Sci. 2014 Nov;348(5):416-22. doi: 10.1097/MAJ.0000000000000335. Am J Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 25250989 Free PMC article.
-
Renin and the (pro)renin receptor in the renal collecting duct: Role in the pathogenesis of hypertension.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2015 Jan;42(1):14-21. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12319. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25371190 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Von Thun AM, Vari RC, El-Dahr SS, Navar LG. Augmentation of intrarenal angiotensin II levels by chronic angiotensin II infusion. Am J Physiol Renal Fluid Electrolyte Physiol. 1994;266:F120–F128. - PubMed
-
- Zou L, Imig JD, Von Thun AM, Hymel A, Ono H, Navar LG. Receptor- mediated intrarenal ANG II augmentation in ANG II-infused rats. Hypertension. 1996;28:669–677. - PubMed
-
- Zou LX, Hymel A, Imig JD, Navar LG. Renal accumulation of circulating angiotensin II in angiotensin II-infused rats. Hypertension. 1996;27:658–662. - PubMed
-
- El-Dahr SS, Dipp S, Guan S, Navar LG. Renin, angiotensinogen, and kallikrein gene expression in two-kidney Goldblatt hypertensive rats. Am J Hypertens. 1993;6:914–919. - PubMed
-
- Moffett RB, McGowan RA, Gross KW. Modulation of kidney renin messenger RNA levels during experimentally induced hypertension. Hypertension. 1986;8:874–882. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

