Prospective study of obstructive sleep apnea and incident coronary heart disease and heart failure: the sleep heart health study
- PMID: 20625114
- PMCID: PMC3117288
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.901801
Prospective study of obstructive sleep apnea and incident coronary heart disease and heart failure: the sleep heart health study
Abstract
Background: Clinic-based observational studies in men have reported that obstructive sleep apnea is associated with an increased incidence of coronary heart disease. The objective of this study was to assess the relation of obstructive sleep apnea to incident coronary heart disease and heart failure in a general community sample of adult men and women.
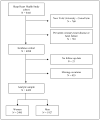
Methods and results: A total of 1927 men and 2495 women > or =40 years of age and free of coronary heart disease and heart failure at the time of baseline polysomnography were followed up for a median of 8.7 years in this prospective longitudinal epidemiological study. After adjustment for multiple risk factors, obstructive sleep apnea was a significant predictor of incident coronary heart disease (myocardial infarction, revascularization procedure, or coronary heart disease death) only in men < or =70 years of age (adjusted hazard ratio 1.10 [95% confidence interval 1.00 to 1.21] per 10-unit increase in apnea-hypopnea index [AHI]) but not in older men or in women of any age. Among men 40 to 70 years old, those with AHI > or =30 were 68% more likely to develop coronary heart disease than those with AHI <5. Obstructive sleep apnea predicted incident heart failure in men but not in women (adjusted hazard ratio 1.13 [95% confidence interval 1.02 to 1.26] per 10-unit increase in AHI). Men with AHI > or =30 were 58% more likely to develop heart failure than those with AHI <5.
Conclusions: Obstructive sleep apnea is associated with an increased risk of incident heart failure in community-dwelling middle-aged and older men; its association with incident coronary heart disease in this sample is equivocal.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Punjabi has received research support from ResMed, Inc., for multi-center clinical trials of CPAP in Type 2 diabetics with sleep apnea, and has received travel support and honoraria for continuing medical education lectures or symposia sponsored by Respironics and ResMed, Inc. Dr. Redline receives CPAP equipment from Philips-Respironics for use in NIH and foundation-supported clinical trials and has been nominated to serve as the first incumbent of an endowed professorship donated to the Harvard Medical School by Dr. Peter Farrell, the founder and Board Chairman of ResMed, Inc., through a charitable remainder trust instrument. All other authors report no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Letter by ng regarding article, "prospective study of obstructive sleep apnea and incident coronary heart disease and heart failure: the sleep heart health study".Circulation. 2011 Mar 22;123(11):e384. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.988857. Circulation. 2011. PMID: 21422395 No abstract available.
References
-
- Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, Skatrud J, Weber S, Badr S. The occurrence of sleep-disordered breathing among middle-aged adults. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1230–1235. - PubMed
-
- Hung J, Whitford EG, Parsons RW, Hillman DR. Association of sleep apnoea with myocardial infarction in men. Lancet. 1990;336:261–264. - PubMed
-
- Saito T, Yoshikawa T, Sakamoto Y, Tanaka K, Inoue T, Ogawa R. Sleep apnea in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Crit Care Med. 1991;19:938–941. - PubMed
-
- Mooe T, Rabben T, Wiklund U, Franklin KA, Eriksson P. Sleep-disordered breathing in men with coronary artery disease. Chest. 1996;109:659–663. - PubMed
-
- Mooe T, Rabben T, Wiklund U, Franklin KA, Eriksson P. Sleep-disordered breathing in women: occurrence and association with coronary artery disease. Am J Med. 1996;101:251–256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01HL53937/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL053916/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL64360/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL063463/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL53938/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL053938/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL053941/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL053937/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL53934/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL064360/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL63429/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL53931/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL53941/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL053934/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL063429/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL53940/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL63463/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL053931/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical