Substance use risk profiles and associations with early substance use in adolescence
- PMID: 20625809
- PMCID: PMC2967704
- DOI: 10.1007/s10865-010-9278-4
Substance use risk profiles and associations with early substance use in adolescence
Abstract
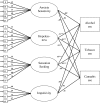
We examined whether anxiety sensitivity, hopelessness, sensation seeking, and impulsivity (i.e., revised version of the Substance Use Risk Profile Scale) would be related to the lifetime prevalence and age of onset of alcohol, tobacco, and cannabis use, and to polydrug use in early adolescence. Baseline data of a broader effectiveness study were used from 3,783 early adolescents aged 11-15 years. Structural equation models showed that hopelessness and sensation seeking were indicative of ever-used alcohol, tobacco or cannabis and for the use of more than one substance. Furthermore, individuals with higher levels of hopelessness had a higher chance of starting to use alcohol or cannabis at an earlier age, but highly anxiety sensitive individuals were less likely to start using alcohol use at a younger age. Conclusively, early adolescents who report higher levels of hopelessness and sensation seeking seem to be at higher risk for an early onset of substance use and poly substance use.
Figures
References
-
- Arnett JJ. Sensation seeking. A new conceptualization and a new scale. Personality and Individual Differences. 1994;16:289–296. doi: 10.1016/0191-8869(94)90165-1. - DOI
-
- Asparouhov T, Muthén B. Exploratory Structural Equation Modeling. Structural Equation Modeling. 2009;16:397–438. doi: 10.1080/10705510903008204. - DOI