Integrative analysis reveals selective 9p24.1 amplification, increased PD-1 ligand expression, and further induction via JAK2 in nodular sclerosing Hodgkin lymphoma and primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 20628145
- PMCID: PMC2995356
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-05-282780
Integrative analysis reveals selective 9p24.1 amplification, increased PD-1 ligand expression, and further induction via JAK2 in nodular sclerosing Hodgkin lymphoma and primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
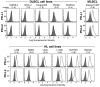
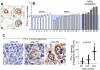
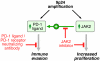
Classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) and mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (MLBCL) are lymphoid malignancies with certain shared clinical, histologic, and molecular features. Primary cHLs and MLBCLs include variable numbers of malignant cells within an inflammatory infiltrate, suggesting that these tumors escape immune surveillance. Herein, we integrate high-resolution copy number data with transcriptional profiles and identify the immunoregulatory genes, PD-L1 and PD-L2, as key targets at the 9p24.1 amplification peak in HL and MLBCL cell lines. We extend these findings to laser-capture microdissected primary Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg cells and primary MLBCLs and find that programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) ligand/9p24.1 amplification is restricted to nodular sclerosing HL, the cHL subtype most closely related to MLBCL. Using quantitative immunohistochemical methods, we document the association between 9p24.1 copy number and PD-1 ligand expression in primary tumors. In cHL and MLBCL, the extended 9p24.1 amplification region also included the Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) locus. Of note, JAK2 amplification increased protein expression and activity, specifically induced PD-1 ligand transcription and enhanced sensitivity to JAK2 inhibition. Therefore, 9p24.1 amplification is a disease-specific structural alteration that increases both the gene dosage of PD-1 ligands and their induction by JAK2, defining the PD-1 pathway and JAK2 as complementary rational therapeutic targets.
Figures
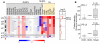
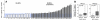

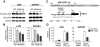
References
-
- Kuppers R. The biology of Hodgkin's lymphoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:15–27. - PubMed
-
- Savage K, Monti S, Kutok J, et al. The molecular signature of mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma differs from that of other diffuse large B-cell lymphomas and shares features with classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 2003;102(12):3871–3879. - PubMed
-
- Gaulard P, Harris NL, Pileri SA, et al. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO Press; 2008. Primary mediastinal (thymic) large B-cell lymphoma. pp. 175–176.
-
- Stein H, von Wasielewski R, Poppema S, MacLennan KA, Guenovva M. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO Press; 2008. Nodular sclerosis classical Hodgkin lymphoma. pp. 249–250.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

