Rapid loss of blood-brain barrier P-glycoprotein activity through transporter internalization demonstrated using a novel in situ proteolysis protection assay
- PMID: 20628400
- PMCID: PMC2949254
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2010.117
Rapid loss of blood-brain barrier P-glycoprotein activity through transporter internalization demonstrated using a novel in situ proteolysis protection assay
Abstract
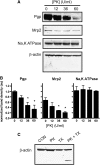
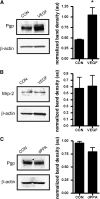
Blood-brain barrier (BBB) P-glycoprotein activity is rapidly reduced by vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) acting via Src and by tumor necrosis factor-alpha acting via protein kinase C (PKC)beta1. To probe underlying mechanism(s), we developed an in vivo, immunoblot-based proteinase K (PK) protection assay to assess the changes in the P-glycoprotein content of the BBB's luminal membrane. Infusion of PK into the brain vasculature selectively cleaved luminal membrane P-glycoprotein, leaving intracellular proteins intact. Intracerebroventricular injection of VEGF partially protected P-glycoprotein from proteolytic cleavage, consistent with transporter internalization. Activation of PKCbeta1 did not protect P-glycoprotein. Thus, VEGF and PKCbeta1 reduce P-glycoprotein activity by distinct mechanisms.
Figures
References
-
- Friedenberg WR, Rue M, Blood EA, Dalton WS, Shustik C, Larson RA, Sonneveld P, Greipp PR. Phase III study of PSC-833 (valspodar) in combination with vincristine, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone (valspodar/VAD) versus VAD alone in patients with recurring or refractory multiple myeloma (E1A95): a trial of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Cancer. 2006;106:830–838. - PubMed
-
- Germann UA, Chambers TC, Ambudkar SV, Licht T, Cardarelli CO, Pastan I, Gottesman MM. Characterization of phosphorylation-defective mutants of human P-glycoprotein expressed in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1996;217:1708–1716. - PubMed
-
- Goodfellow HR, Sardini A, Ruetz S, Callaghan R, Gros P, McNaughton PA, Higgins CF. Protein kinase C-mediated phosphorylation does not regulate drug transport by the human multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:13668–13674. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

