The role of primary care clinicians in diagnosing and treating bipolar disorder
- PMID: 20628500
- PMCID: PMC2902189
- DOI: 10.4088/PCC.9064su1c.01
The role of primary care clinicians in diagnosing and treating bipolar disorder
Abstract
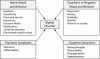
Because many patients with bipolar disorder seek treatment in primary care practices, physicians in these settings need to be able to diagnose bipolar disorder and common psychiatric and medical comorbidities and to initiate and manage treatment. Unfortunately, bipolar disorder is often underrecognized. The most common symptoms in patients with bipolar disorder are depressive, but these patients may also have anxiety, mood swings, sleep problems, irritability, difficulty concentrating, relationship issues, alcohol- or drug-related problems, and infections. Social and family history and screening tools can help clarify diagnosis. The goal of treatment should be recovery, but periodic relapse and medication nonadherence should be expected. Primary care physicians should decide what level of intervention their practices can support. To manage these patients effectively, practices may need to train office staff, set up monitoring and follow-up systems, establish links with referral and community support services, develop therapeutic alliances with patients, and provide psychoeducation for patients and significant others. Receiving comprehensive psychiatric and medical care and support can be life-changing for patients with bipolar disorder and their families.
Figures
References
-
- Regier DA, Narrow WE, Rae DS, et al. The de facto US mental and addictive disorders service system: Epidemiologic Catchment Area prospective 1-year prevalence rates of disorders and services. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1993;50(2):85–94. - PubMed
-
- Wang PS, Berglund P, Olfson M, et al. Failure and delay in initial treatment contact after first onset of mental disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(6):603–613. - PubMed
-
- Manning JS, Haykal RF, Connor PD, et al. On the nature of depressive and anxious states in a family practice setting: the high prevalence of bipolar II and related disorders in a cohort followed longitudinally. Compr Psychiatry. 1997;38(2):102–108. - PubMed
-
- Goodwin FK, Jamison K.R. Manic-Depressive Illness. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 1990.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
