Effects of sulfur amino acids, L: -methionine, L: -cystine and L: -cysteine on lipoprotein lipase and hormone-sensitive lipase in differentiated mouse 3T3-L1 adipocytes
- PMID: 20628900
- PMCID: PMC2932907
- DOI: 10.1007/s10616-010-9282-0
Effects of sulfur amino acids, L: -methionine, L: -cystine and L: -cysteine on lipoprotein lipase and hormone-sensitive lipase in differentiated mouse 3T3-L1 adipocytes
Abstract
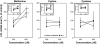
Rats subcutaneously implanted with AH109A hepatoma cells show hyperlipidemia with high concentrations of serum triglyceride and nonesterified fatty acid, suppression of lipoprotein lipase (LPL), and elevation of hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) activities during the growth of the hepatoma. Supplementation of the diet with sulfur amino acids such as L: -methionine (Met) and L: -cystine (Cys) improved hyperlipidemia by restoring LPL and HSL activities. In the present study, we have attempted to examine the effects of sulfur amino acids on the activity and mRNA level of LPL and the activity of HSL using 3T3-L1 cells, which are known to differentiate to adipocytes. The adipocytes were incubated with various concentrations of Met, Cys or L: -cysteine (CysH) in the absence or presence of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha). LPL activity was suppressed by TNF-alpha. In the absence of TNF-alpha, Met, Cys and CysH did not change the LPL activity. In the presence of TNF-alpha, Met and Cys significantly increased the LPL activity, and Met also enhanced the LPL mRNA level. HSL activity was also suppressed by TNF-alpha. In the absence of TNF-alpha, Met enhanced the HSL activity. In the presence of TNF-alpha, Met, Cys and CysH suppressed the HSL activity. Sulfur amino acids such as Met, Cys and CysH affected the LPL activity, mRNA level, and HSL activity in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Some of these effects of sulfur amino acids were different between LPL and HSL, between the absence and the presence of TNF-alpha, and between 3T3-L1 adipocytes and the adipose tissue from rats.
Figures

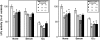
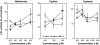

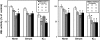

Similar articles
-
Effects of simultaneous dietary fish oil ingestion and sulfur amino acid supplementation on the lipid metabolism in hepatoma-bearing rats with hyperlipidemia.J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2010;56(4):247-54. doi: 10.3177/jnsv.56.247. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2010. PMID: 20924147
-
TNF-α decreases lipoprotein lipase activity in 3T3-L1 adipocytes by up-regulation of angiopoietin-like protein 4.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2017 May;1862(5):533-540. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2017.02.005. Epub 2017 Feb 13. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2017. PMID: 28215713
-
Effects of dietary methionine and cystine on lipid metabolism in hepatoma-bearing rats with hyperlipidemia.Lipids. 1998 Sep;33(9):905-11. doi: 10.1007/s11745-998-0287-6. Lipids. 1998. PMID: 9778138
-
Insulin and rosiglitazone regulation of lipolysis and lipogenesis in human adipose tissue in vitro.Diabetes. 2002 May;51(5):1493-8. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.51.5.1493. Diabetes. 2002. PMID: 11978647
-
Characterization of differentiation factor/leukaemia inhibitory factor effect on lipoprotein lipase activity and mRNA in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.Cytokine. 1994 Jul;6(4):425-32. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(94)90067-1. Cytokine. 1994. PMID: 7948751
Cited by
-
MASLD: insights on the role of folate in hepatic lipid metabolism.Front Nutr. 2025 Jul 16;12:1583674. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1583674. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40740648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increase or decrease hydrogen sulfide exert opposite lipolysis, but reduce global insulin resistance in high fatty diet induced obese mice.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 13;8(9):e73892. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073892. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24058499 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barclay M, Skipski VP, Terebus-Kekish O, Greene EM, Kaufman RJ, Stock CC. Effects of cancer upon high-density and other lipoproteins. Cancer Res. 1970;30:2420–2430. - PubMed
-
- Grunfeld C, Gulli R, Moser AH, Gavin LA, Feingold KR. Effect of tumor necrosis factor administration in vivo on lipoprotein lipase activity in various tissues of the rat. J Lipid Res. 1989;30:579–585. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

