Comparison of glucose derivatives effects on cartilage degradation
- PMID: 20630114
- PMCID: PMC3161396
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-11-162
Comparison of glucose derivatives effects on cartilage degradation
Abstract
Background: Glucosamine (GlcN) is a well-recognized candidate for treatment of osteoarthritis. However, it is currently used in derivative forms, such as glucosamine-hydrochloride (GlcN-HCl) or glucosamine sulfate (GlcN-S). However, the molecular mode of action remains unclear. In this study, we compared the effects of Glucose (Glc), Glucuronic acid (GlcA), Glucosamine hydrochloride (GlcN-HCl) and Glucosamine sulfate (GlcN-S) on cartilage degradation.
Methods: Porcine cartilage explants were co-cultured with recombinant human IL-1beta and each tested substance for 3 days. HA, s-GAG and MMP-2 releases to media were measured using ELISA, dye-binding assay and gelatin zymography, respectively. Similar studies were performed in a human articular chondrocytes (HAC) monolayer culture, where cells were co-treated with IL-1beta and each reagent for 24 hours. Subsequently, cells were harvested and gene expression measured using RT-PCR. All experiments were carried out in triplicate. Student's t-tests were used for statistical analysis.
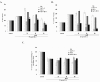
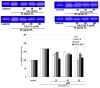
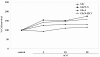
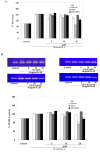
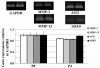
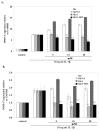
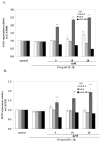
Results: In cartilage explants treated with IL-1beta, GlcN-S had the highest chondroprotective activity of all four chemicals as shown by the inhibition of HA, s-GAG and MMP-2 released from cartilage. The anabolic (aggrecan core protein; AGG, SOX9) and catabolic (MMP-3, -13) genes in HACs treated with IL-1beta and with/without chemicals were studied using RT-PCR. It was found that, GlcN-HCl and GlcN-S could reduce the expression of both MMP-3 and -13 genes. The IL-1beta induced-MMP-13 gene expression was decreased maximally by GlcN-S, while the reduction of induced-MMP-3 gene expression was greatest with GlcN-HCl. Glc and GlcA reversed the effect of IL-1beta on the expression of AGG and SOX9, but other substances had no effect.
Conclusion: This study shows that glucosamine derivatives can alter anabolic and catabolic processes in HACs induced by IL-1beta. GlcN-S and GluN-HCl decreased induced MMP-3 and -13 expressions, while Glc and GlcA increased reduced-AGG and SOX9 expression. The chondroprotective study using porcine cartilage explant showed that GlcN-S had the strongest effect.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glucosamine reduces anabolic as well as catabolic processes in bovine chondrocytes cultured in alginate.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007 Nov;15(11):1267-74. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2007.04.004. Epub 2007 May 31. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007. PMID: 17543549
-
Glucosamine decreases expression of anabolic and catabolic genes in human osteoarthritic cartilage explants.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006 Mar;14(3):250-7. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2005.10.001. Epub 2005 Nov 18. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006. PMID: 16300972
-
Glucosamine promotes chondrogenic phenotype in both chondrocytes and mesenchymal stem cells and inhibits MMP-13 expression and matrix degradation.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007 Jun;15(6):646-55. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2007.01.014. Epub 2007 Mar 6. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007. PMID: 17337215
-
Biological activities of glucosamine and its related substances.Adv Food Nutr Res. 2012;65:337-52. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-416003-3.00022-6. Adv Food Nutr Res. 2012. PMID: 22361198 Review.
-
Glucosamine as a Treatment for Osteoarthritis: What If It's True?Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 17;13:820971. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.820971. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35370756 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Optimization of a chondrogenic medium through the use of factorial design of experiments.Biores Open Access. 2012 Dec;1(6):306-13. doi: 10.1089/biores.2012.0277. Biores Open Access. 2012. PMID: 23514743 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of coculturing canine notochordal, nucleus pulposus and mesenchymal stromal cells for intervertebral disc regeneration.Arthritis Res Ther. 2015 Mar 14;17(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0569-6. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 25890127 Free PMC article.
-
Andrographolide Exerts Chondroprotective Activity in Equine Cartilage Explant and Suppresses Interleukin-1 β -Induced MMP-2 Expression in Equine Chondrocyte Culture.Int Sch Res Notices. 2014 Oct 29;2014:464136. doi: 10.1155/2014/464136. eCollection 2014. Int Sch Res Notices. 2014. PMID: 27379277 Free PMC article.
-
Glucosamine Hydrochloride but Not Chondroitin Sulfate Prevents Cartilage Degradation and Inflammation Induced by Interleukin-1α in Bovine Cartilage Explants.Cartilage. 2016 Jan;7(1):70-81. doi: 10.1177/1947603515603762. Cartilage. 2016. PMID: 26958319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Setnikar I, Cereda R, Pacini MA, Revel L. Antireactive properties of glucosamine sulfate. Arzneimittelforschung. 1991;41:157–61. - PubMed
-
- Lopes Vaz A. Double-blind clinical evaluation of the relative efficacy of ibuprofen and glucosamine sulphate in the management of osteoarthrosis of the knee in out-patients. Curr Med Res Opin. 1982;8:145–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

