The in vivo performance of plasmonic nanobubbles as cell theranostic agents in zebrafish hosting prostate cancer xenografts
- PMID: 20630586
- PMCID: PMC2924909
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.06.031
The in vivo performance of plasmonic nanobubbles as cell theranostic agents in zebrafish hosting prostate cancer xenografts
Abstract
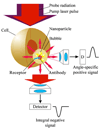
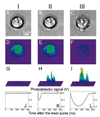
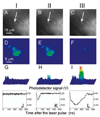
Cell theranostics is a new approach that unites diagnosis, therapy and confirmation (guidance) of the results of therapy in one single process at cell level, thus principally improving both the rapidity and precision of treatment. The ideal theranostic agent will support all three of the above functions in vivo with cellular resolution, allowing individual assessment of disease state and the elimination of diseased cells while leaving healthy cells intact. We have developed and evaluated plasmonic nanobubbles (PNBs) as an in vivo tunable theranostic cellular agent in zebrafish hosting prostate cancer xenografts. PNBs were selectively generated around gold nanoparticles in cancer cells in the zebrafish with short single laser pulses. By varying the energy of the laser pulse, we dynamically tuned the PNB size in a theranostic sequence of two PNBs: an initial small PNB detected a cancer cell through optical scattering, followed by a second bigger PNB, which mechanically ablated this cell without damage to surrounding tissue, while its optical scattering confirmed the destruction of the cell. Thus PNBs supported the diagnosis and guided ablation of individual human cancer cells in a living organism without damage to the host.
2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tunable plasmonic nanobubbles for cell theranostics.Nanotechnology. 2010 Feb 26;21(8):85102. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/21/8/085102. Epub 2010 Jan 25. Nanotechnology. 2010. PMID: 20097970 Free PMC article.
-
Generation and detection of plasmonic nanobubbles in zebrafish.Nanotechnology. 2010 Jun 4;21(22):225102. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/21/22/225102. Epub 2010 May 7. Nanotechnology. 2010. PMID: 20453288 Free PMC article.
-
Selective and self-guided micro-ablation of tissue with plasmonic nanobubbles.J Surg Res. 2011 Mar;166(1):e3-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2010.10.039. Epub 2010 Nov 26. J Surg Res. 2011. PMID: 21176913 Free PMC article.
-
Methods for Generation and Detection of Nonstationary Vapor Nanobubbles Around Plasmonic Nanoparticles.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1530:165-192. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6646-2_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28150203 Review.
-
Tunable nanostructures as photothermal theranostic agents.Ann Biomed Eng. 2012 Feb;40(2):438-59. doi: 10.1007/s10439-011-0472-5. Epub 2011 Dec 2. Ann Biomed Eng. 2012. PMID: 22134466 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasmonic nanobubbles rapidly detect and destroy drug-resistant tumors.Theranostics. 2012;2(10):976-87. doi: 10.7150/thno.5116. Epub 2012 Oct 13. Theranostics. 2012. PMID: 23139725 Free PMC article.
-
Rainbow Plasmonic Nanobubbles: Synergistic Activation of Gold Nanoparticle Clusters.J Nanomed Nanotechnol. 2011 Jan 1;2(104):1-8. doi: 10.4172/2157-7439.1000104. J Nanomed Nanotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21804947 Free PMC article.
-
Tunable plasmonic nanoprobes for theranostics of prostate cancer.Theranostics. 2011 Jan 10;1:3-17. doi: 10.7150/thno/v01p0003. Theranostics. 2011. Retraction in: Theranostics. 2017 Jan 7;7(3):561. doi: 10.7150/thno.18746. PMID: 21547151 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Plasmonic nanobubbles enhance efficacy and selectivity of chemotherapy against drug-resistant cancer cells.Adv Mater. 2012 Jul 24;24(28):3831-7. doi: 10.1002/adma.201103550. Epub 2012 Mar 7. Adv Mater. 2012. PMID: 22407874 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Quo natas, Danio?-Recent Progress in Modeling Cancer in Zebrafish.Front Oncol. 2017 Aug 28;7:186. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00186. eCollection 2017. Front Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28894696 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McCarthy JR. The future of theranostic nanoagents. Nanomedicine. 2009;4:693–695. - PubMed
-
- Hartman KB, Wilson LJ, Rosenblum MG. Detecting and treating cancer with nanotechnology. Mol Diagn Ther. 2008;12:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Picard FJ, Bergeron MG. Rapid molecular theranostics in infectious diseases. Drug Discov Today. 2002;7:1092–1101. - PubMed
-
- Al-Jamal WT, Al-Jamal KT, Tian B, Cakebread A, Halket JM, Kostarelos K. Tumor targeting of functionalized quantum dot-liposome hybrids by intravenous administration. Mol Pharm. 2009;6:520–530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

