Gr-1+CD11b+ myeloid cells tip the balance of immune protection to tumor promotion in the premetastatic lung
- PMID: 20631080
- PMCID: PMC4675145
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0706
Gr-1+CD11b+ myeloid cells tip the balance of immune protection to tumor promotion in the premetastatic lung
Abstract
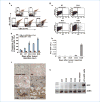
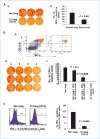
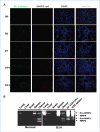
The mechanisms by which a primary tumor affects a selected distant organ before tumor cell arrival remain to be elucidated. This report shows that Gr-1+CD11b+ cells are significantly increased in lungs of mice bearing mammary adenocarcinomas before tumor cell arrival. In the premetastatic lungs, these immature myeloid cells significantly decrease IFN-gamma production and increase proinflammatory cytokines. In addition, they produce large quantities of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9) and promote vascular remodeling. Deletion of MMP9 normalizes aberrant vasculature in the premetastatic lung and diminishes lung metastasis. The production and activity of MMP9 is selectively restricted to lungs and organs with a large number of Gr-1+CD11b+ cells. Our work reveals a novel protumor mechanism for Gr-1+CD11b+ cells that changes the premetastatic lung into an inflammatory and proliferative environment, diminishes immune protection, and promotes metastasis through aberrant vasculature formation. Thus, inhibition of Gr-1+CD11b+ cells could normalize the premetastatic lung environment, improve host immunosurveillance, and inhibit tumor metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures



References
-
- Steeg PS. Tumor metastasis: mechanistic insights and clinical challenges. Nat Med. 2006;12:895–904. - PubMed
-
- Hynes RO. Metastatic potential: generic predisposition of the primary tumor or rare, metastatic variants-or both? Cell. 2003;113:821–3. - PubMed
-
- Kang Y, Siegel PM, Shu W, et al. A multigenic program mediating breast cancer metastasis to bone. Cancer Cell. 2003;3:537–49. - PubMed
-
- Gupta GP, Massague J. Cancer metastasis: building a framework. Cell. 2006;127:679–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

