Associations of proinflammatory cytokine levels with lipid profiles, growth, and body composition in HIV-infected children initiating or changing antiretroviral therapy
- PMID: 20631646
- PMCID: PMC2991416
- DOI: 10.1097/INF.0b013e3181ed9f4c
Associations of proinflammatory cytokine levels with lipid profiles, growth, and body composition in HIV-infected children initiating or changing antiretroviral therapy
Abstract
Objectives: To measure proinflammatory cytokines (PIC) in HIV-infected children beginning or changing antiretroviral therapy (ART), evaluating associations with virologic, immunologic, serum lipid, growth, and body composition measures, markers of growth hormone action and glucose metabolism.
Methods: Forty-nine prepubertal HIV-infected children had measurements of viral load (VL), CD4 lymphocyte count and percentage, serum lipids, apolipoprotein AI/B, IGF-1, IGFBP-1, and IGFBP-3, anthropometry, bioelectrical impedance analysis, TNF-α, IL-1 β, and IL-6 at baseline and 48 weeks of ART.
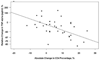
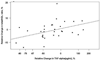
Results: Baseline levels were detectable (>0.1 pg/mL) for IL-1 β in 28 of 48, and for TNF-α and Il-6 in all 49 children. TNF-α decreased with ART (P < 0.001) and IL-6 demonstrated a similar trend (P = 0.065). Children with 48-week VL <400 copies/mL had greater declines in TNF-α (mean 45%) than subjects with higher VL (5%; P = 0.009). Each 10% improvement in CD4% was associated with 26% lower TNF-α (P = 0.002) and 31% lower IL-6 (P = 0.016). Greater reductions in TNF-α were associated with lower total/HDL cholesterol ratio (P = 0.003) at week 48.
Conclusions: In HIV-infected children initiating or changing ART, PIC were detectable at baseline and decreased over 48 weeks. Better immunologic responses were associated with greater reductions in TNF-α and IL-6. Reductions in TNF-α were associated with improved total/HDL cholesterol ratio.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant conflicts.
Figures


References
-
- Cunningham-Rundles S, Kim S, Dnistrian A, Noroski L, Mendez-Botet C, Grassey C, Hinds G, Cervia J. Micronutrient and cytokine interaction in congenital pediatric HIV infection. J Nutr. 1996;126:2674S–2679S. - PubMed
-
- Johann-Liang R, O’Neill L, Cervia J, Haller I, Giunta Y, Licholai T, Noel G. Energy balance, viral burden, insulin-like growth factor-1, interleukin-6 and growth impairment in children infected with human immunodeficiency virus. AIDS. 2000;14(6):683–690. - PubMed
-
- Brazille P, Dereuddre-Bosquet N, Leport C, Clay Boyer P, Vilde J-L, Dormont D, Benveniste O. Decreases on plasma TNF-alpha level and IFN-gamma mRNA level in mononuclear cells (PBMC) and an increase in IL-2 mRNA in PBMC are associated with highly active antiretroviral therapy in HIV-infected patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 2003;131(2):304–311. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aukrust P, Muller F, Lien E, Nordoy I, Liabakk N-B, Kvale D, Espevik T, Froland S. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) system levels in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients during highly active antiretroviral therapy: Persistent TNF activation is associated with virologic and immunologic treatment failure. J Infect Dis. 1999;179:74–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

