The Thomsen-Friedenreich antigen-binding lectin jacalin interacts with desmoglein-1 and abrogates the pathogenicity of pemphigus foliaceus autoantibodies in vivo
- PMID: 20631728
- PMCID: PMC3161408
- DOI: 10.1038/jid.2010.209
The Thomsen-Friedenreich antigen-binding lectin jacalin interacts with desmoglein-1 and abrogates the pathogenicity of pemphigus foliaceus autoantibodies in vivo
Abstract
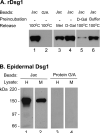
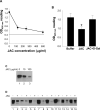
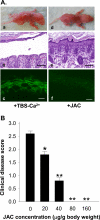
Pemphigus foliaceus (PF) is an autoimmune skin blistering disease mediated by pathogenic autoantibodies against the desmosomal core glycoprotein desmoglein-1 (Dsg1). This study demonstrated that the O-glycan-specific plant lectin jacalin binds Dsg1 and inhibits the interaction of Dsg1/PF IgG. N-glycosylation is not involved in the interaction of Dsg1/jacalin or Dsg1/PF IgG. Subcutaneous injection of jacalin into neonatal mice drastically reduced PF IgG deposition at the epidermal cell surface and blocked PF IgG-induced skin blisters, both clinically and histologically. Interestingly, another plant lectin, peanut agglutinin, which shares the same carbohydrate specificity toward the O-linked carbohydrate structure known as Thomsen-Friedenreich antigen (TF antigen, Galβ1-3GalNAcα-O-Ser/Thr), also bound Dsg1 and blocked the skin blistering. In contrast, the plant lectin vicia villosa-B4 (VVL-B4), which shares the carbohydrate specificity toward the O-linked monosaccharide known as Thomsen-nouveau antigen (GalNAc-α1-O-Ser/Thr), did not bind Dsg1 and did not show a protective effect against the disease induced by the autoantibodies. Collectively, these results suggest that the binding of jacalin to O-linked TF carbohydrate motifs on Dsg1 impairs the Dsg1/PF autoantibody interactions and abrogates its pathogenicity in vivo. TF-specific binding ligands may have a potential therapeutic value for PF.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Non-pathogenic pemphigus foliaceus (PF) IgG acts synergistically with a directly pathogenic PF IgG to increase blistering by p38MAPK-dependent desmoglein 1 clustering.J Dermatol Sci. 2017 Mar;85(3):197-207. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2016.12.010. Epub 2016 Dec 12. J Dermatol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28024684 Free PMC article.
-
Endocytosis of IgG, Desmoglein 1, and Plakoglobin in Pemphigus Foliaceus Patient Skin.Front Immunol. 2019 Nov 12;10:2635. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02635. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31781120 Free PMC article.
-
The plant lectin wheat germ agglutinin inhibits the binding of pemphigus foliaceus autoantibodies to desmoglein 1 in a majority of patients and prevents pathomechanisms of pemphigus foliaceus in vitro and in vivo.J Immunol. 2003 Dec 1;171(11):6244-50. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.11.6244. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14634141
-
Pemphigus foliaceus.Curr Dir Autoimmun. 2008;10:182-94. doi: 10.1159/000131454. Curr Dir Autoimmun. 2008. PMID: 18460886 Review.
-
A perspective of pemphigus from bedside and laboratory-bench.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2007 Oct;33(1-2):57-66. doi: 10.1007/s12016-007-0036-5. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2007. PMID: 18094947 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathogenic IgG4 autoantibodies from endemic pemphigus foliaceus recognize a desmoglein-1 conformational epitope.J Autoimmun. 2018 May;89:171-185. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2017.12.017. Epub 2018 Jan 4. J Autoimmun. 2018. PMID: 29307589 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amagai M, Hashimoto T, Green KJ, Shimizu N, Nishikawa T. Antigen-specific immunoadsorption of pathogenic autoantibodies in pemphigus foliaceus. J Invest Dermatol. 1995a;104:895–901. - PubMed
-
- Amagai M, Ishii K, Hashimoto T, Gamou S, Shimizu N, Nishikawa T. Conformational epitopes of pemphigus antigens (Dsg1 and Dsg3) are calcium dependent and glycosylation independent. J Invest Dermatol. 1995b;105:243–247. - PubMed
-
- Anhalt GJ, Labib RS, Voorhees JJ, Beals TF, Diaz LA. Induction of pemphigus in neonatal mice by passive transfer of IgG from patients with the disease. N Engl J Med. 1982;306:1189–1196. - PubMed
-
- Aoki V, Millikan RC, Rivitti EA, Hans-Filho G, Eaton DP, Warren SJ, et al. Environmental risk factors in endemic pemphigus foliaceus (fogo selvagem). J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2004;9:34–40. - PubMed
-
- Arockia Jeyaprakash A, Jayashree G, Mahanta SK, Swaminathan CP, Sekar K, Surolia A, et al. Structural basis for the energetics of jacalin-sugar interactions: promiscuity versus specificity. J Mol Biol. 2005;347:181–188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI061430/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R29 AI040768/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI040768/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AR32599/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR053313/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR032599/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR052109/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI61430/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR032081/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI40768/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AR30281/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AR052109/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AR053313/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

